Acupuncture for chronic insomnia disorder: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
- PMID: 40371085
- PMCID: PMC12074954
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1541276
Acupuncture for chronic insomnia disorder: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of placebo response to acupuncture on subjective and objective sleep indices in patients with chronic insomnia disorder and to understand the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of chronic insomnia disorder (CID).
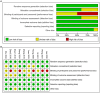
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted from the inception of the databases to March 17, 2025, encompassing eight databases. A randomized controlled pilot study of collecting acupuncture versus sham acupuncture for the treatment of CID. Systematic collection of acupuncture therapies for CID was performed based on randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Independent researchers critically reviewed the literature, recorded relevant data, and assessed the quality of research. Data were analyzed using RevMan 5.3, Stata 17.0, and TSA 0.9.5.10.
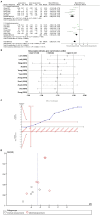
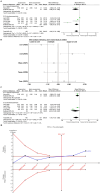
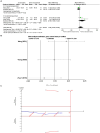
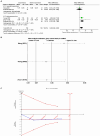
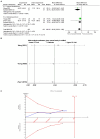
Results: The study included a total of 757 patients across 10 trials. Acupuncture demonstrated significant improvement in PSQI scores [MD = -2.60, 95% CI = (-3.24, -1.97), p < 0.00001] and ISI scores (MD = -2.04, 95% CI = [-3.18, -0.90], p = 0.0005) compared to sham acupuncture. Sequential analyses of the trials showed stable results. Subgroup analyses showed that manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture were superior to sham acupuncture in improving PSQI scores [MD = -3.85, 95% CI = (-4.94, -2.76), p < 0.00001; MD = -1.67, 95% CI = (-2.25, -1.08), p < 0.00001]. Manual acupuncture and electroacupuncture were superior to sham acupuncture in improving ISI scores [MD = -2.60, 95% CI = (-4.72, -0.48), p = 0.02; MD = -1.93, 95% CI = (-3.16, -0.71), p = 0.002]. In terms of objective sleep indices, there was no statistically significant difference in total sleep time between acupuncture and sham acupuncture [MD = 11.92, 95% CI = (-20.25, 44.09), p = 0.47]. Acupuncture was superior to sham acupuncture in terms of sleep efficiency and wake after sleep onset [MD = 3.62, 95% CI = (0.92, 6.32), p = 0.009; MD = -18.53, 95% CI = (-29.22, -7.85), p = 0.0007]. However, the sequential analysis indicated limitations due to small sample size which hindered drawing definitive conclusions.
Conclusion: Compared with sham acupuncture, acupuncture is effective in improving subjective sleep quality in patients with CID. However, whether acupuncture improves patients' objective sleep indices compared to sham acupuncture is uncertain and more high-quality clinical trial evidence is needed to validate this.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, Identifier CRD42024541760.
Keywords: acupuncture; chronic insomnia disorder; meta-analysis; systematic review; trial sequential analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Li, Zhu, Wang, Xi, Qiu, Xu, Liang, Guo and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

