The economical role of RIOK3 in modulating the Jak1/STAT1 pathway and antiviral immunity against respiratory syncytial virus infection in macrophages: implications for therapeutic potential
- PMID: 40371100
- PMCID: PMC12075202
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1591473
The economical role of RIOK3 in modulating the Jak1/STAT1 pathway and antiviral immunity against respiratory syncytial virus infection in macrophages: implications for therapeutic potential
Abstract
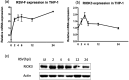
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a leading cause of lower respiratory tract infections, particularly in vulnerable populations such as infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. RSV infection can result in mortality rates as high as 20%, attributable not only to viral replication but also to an excessive host immune response. Current therapeutic options are limited, partly due to gaps in understanding the host immune response, especially the role of macrophages and their signaling pathways. This study investigates the role of RIOK3, an unconventional kinase, in modulating the Jak1/STAT1 pathway during RSV infection in macrophages and its impact on viral replication and interferon production. Using both in vitro and in vivo models, including primary bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM) from control and RIOK3 knockout (KO) mice, we demonstrate that RIOK3 is a critical regulator of the Jak1/STAT1 pathway in macrophages during RSV infection. The absence of RIOK3 enhances viral replication and disrupts the balance of type I interferons. Targeting RIOK3 may represent a promising strategy to enhance antiviral immunity and mitigate RSV-induced inflammation, thus warranting further investigation for therapeutic potential.
Keywords: Jak1/STAT pathway; RIOK3; RSV; macrophage; type I interferon.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Liang, Qian and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

