Role and mechanisms of m6A demethylases in digestive system tumors
- PMID: 40371134
- PMCID: PMC12070089
- DOI: 10.62347/XMAF1290
Role and mechanisms of m6A demethylases in digestive system tumors
Abstract
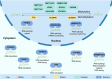
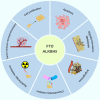
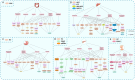
Digestive system tumors are common malignancies in humans, often accompanied by high mortality and poor prognosis. Therefore, intensive research on the pathogenesis of digestive system tumors is imperative. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common RNA modification in eukaryotes and exerts regulatory effects on RNA expression and metabolism, including splicing, translation, stability, decay, and transport. m6A demethylases belong to the AlkB family of dioxygenases that can catalyze m6A demethylation. Accumulating evidence in recent years has shown that abnormal m6A levels caused by m6A demethylases play crucial roles in different aspects of human cancer development. In this review, we comprehensively summarize the recent findings on the functions and underlying molecular mechanisms of m6A demethylases in cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy, and the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) of digestive system tumors. Furthermore, we discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting these m6A demethylases for treatment.
Keywords: AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5); cancer therapeutics; digestive system tumors; fat mass and obesity associated protein (FTO); m6A.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging Roles of N6-Methyladenosine Demethylases and Its Interaction with Environmental Toxicants in Digestive System Cancers.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Sep 9;13:7101-7114. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S328188. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34526822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of m6A Demethylases Inhibitors and Their Biological Functions in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5815. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105815. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of N6-methyladenosine modification on metabolic reprogramming in digestive tract tumors.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 11;10(2):e24414. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24414. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Seq data of ALKBH5 and FTO double knockout HEK293T human cells.Data Brief. 2022 Apr 20;42:108187. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108187. eCollection 2022 Jun. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35516002 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct RNA N-demethylation pathways catalyzed by nonheme iron ALKBH5 and FTO enzymes enable regulation of formaldehyde release rates.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 13;117(41):25284-25292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007349117. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32989163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Latif M, Townsend K, Dearman C, Shiu KK, Khan K. Immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer: the current scenario and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020;88:102030. - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, Sorek R, Rechavi G. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
