Long noncoding RNA VPS9D1-AS1 promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by regulating the VEGFA signalling pathway
- PMID: 40371141
- PMCID: PMC12070094
- DOI: 10.62347/BKUV1210
Long noncoding RNA VPS9D1-AS1 promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by regulating the VEGFA signalling pathway
Abstract
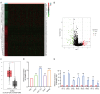
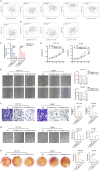
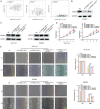
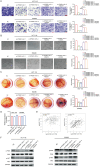
To clarify the mechanism of long non-coding RNA VPS9D1-AS1 affecting angiogenesis in colorectal cancer (CRC). Western blot and qRT-PCR assays were performed to detect the expression of VPS9D1-AS1 in colorectal cancer. The effects of VPS9D1-AS1 regulating VEGFA and affecting the proliferation, migration and invasion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were examined using cell biology, in vitro tubeformation and Chorioallantoic membrane vascular assay. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and dual luciferase assays were performed to verify the specific sites of transcription factor binding to the promoter region of VPS9D1-AS1. VPS9D1-AS1 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer. Interfering with VPS9D1-AS1 inhibited the proliferation, invasion and migration of HUVECs. Mechanistically, VPS9D1-AS1 can promote angiogenesis by upregulating VEGFA expression and activating the downstream PI3K/AKT pathway. In addition, CEBPB is a transcription factor of VPS9D1-AS1 predicted by database, and the results of ChIP experiments showed that CEBPB could directly bind to the VPS9D1-AS1 promoter region at the -698 bp to -794 bp site. The results of dual luciferase assay showed that CEBPB could enhance VPS9D1-AS1 promoter activity and promote its transcription. VPS9D1-AS1 can be activated by CEBPB transcription factor and target VEGFA to activate its downstream pathway to promote colorectal cancer angiogenesis, which may suggest that VPS9D1-AS1 is critical for regulating colorectal cancer angiogenesis.
Keywords: CEBPB; Colorectal cancer; VEGFA; VPS9D1-AS1; angiogenesis.
AJCR Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Si H, Yang Q, Hu H, Ding C, Wang H, Lin X. Colorectal cancer occurrence and treatment based on changes in intestinal flora. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;70:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
