Utility of Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-spectrometry in Evaluating Bone Health in Patients With Spondylarthritis
- PMID: 40371185
- PMCID: PMC12075990
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.84069
Utility of Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-spectrometry in Evaluating Bone Health in Patients With Spondylarthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by reduced bone strength and increased fracture risk, frequently coexists with spondyloarthritis (SpA), an inflammatory rheumatic disease. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis, faces limitations in SpA patients due to spinal deformities and calcifications. Some studies have shown overestimation of BMD values, especially in individuals with syndesmophytic bridges and coexistent mechanical modifications such as osteophytes and discopathic lesions.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was performed to compare the results of bone mineral density (BMD) lumbar spine evaluations performed with Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-spectrometry (REMS) between a control group and a group of patients recently diagnosed with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) who did not follow any specific treatment. All study participants were informed about the objectives, examinations performed, and the use of anonymous data in databases to conduct statistical analyses and publish findings in reference medical scientific journals.
Results: The ratio between male and female participants differed between the study groups. No significant differences were observed between the control and SpA groups, in both female and male subjects, with regard to BMD values. When factoring in the age of the patients, it was observed that the mean age of the control group was 55.53 years, while that of the SpA group was 36.96 years. This suggests that the BMD values of younger SpA patients were equivalent to those of older individuals in the control group.
Conclusion: REMS is a useful tool for evaluating BMD both in the general population and in SpA patients. Furthermore, the lack of any statistically significant correlation between the control and SpA groups confirms that the rheumatic disease influences lumbar bone mineralization. Also, similar BMD values were observed between the groups, despite significantly different mean ages, supporting the conclusion that bone degradation appears early in the evolution of SpA and can be correctly identified using REMS.
Keywords: bone mineral density; dual x-ray absorptiometry; fragility fracture; radiofrequency echographic multispectrometry; spondylarthritis.
Copyright © 2025, Badea et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Cantacuzino Clinical Hospital Ethics Committee issued approval NA. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

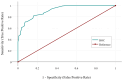
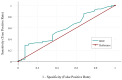


Similar articles
-
Could radiofrequency echographic multispectrometry (REMS) overcome the overestimation in BMD by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at the lumbar spine?BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 May 19;23(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05430-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35590362 Free PMC article.
-
The Advantages of Radiofrequency Echographic MultiSpectrometry in the Evaluation of Bone Mineral Density in a Population with Osteoarthritis at the Lumbar Spine.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;14(5):523. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050523. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38472995 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency Echographic Multispectrometry (REMS) can Overcome the Effects of Structural Internal Artifacts and Evaluate Bone Fragility Accurately.Calcif Tissue Int. 2024 Mar;114(3):246-254. doi: 10.1007/s00223-023-01167-z. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024. PMID: 38127125
-
Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis: state of the art.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Jun 21;36(1):135. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02784-w. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 38904870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry-A Novel Tool in the Diagnosis of Osteoporosis and Prediction of Fragility Fractures: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;15(5):555. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050555. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075802 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Literature review of Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-Spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis of osteoporosis and bone fragility. Badea I, Bojincă M, Milicescu M, Vutcanu O, Ilina AR. Rom J Rheumatol. 2022;32
-
- POS0296: Radiofrequency Echographic Multi-Spectrometry (REMS) and DXA for the evaluation of bone mineral density in axial spondyloarthritis. Fassio A, Pollastri F, Benini C, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83:470.
-
- FRI0196: traditional DXA underestimates bone mineral density of the spine in axial spondyloarthropathy. Fitzgerald G, Anachebe T, O' Shea F. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:639.
-
- A novel quantitative method for estimating bone mineral density using B-mode ultrasound and radiofrequency signals-a pilot study on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Bojincă VC, Popescu CC, Decianu RD, Dobrescu A, Bălănescu ȘM, Bălănescu AR, Bojincă M. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18:1661–1668. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
