Development of Suspended Droplet Microextraction Method for Spectrophotometric Determination of Serum Iron
- PMID: 40371266
- PMCID: PMC12077757
- DOI: 10.1002/ansa.70022
Development of Suspended Droplet Microextraction Method for Spectrophotometric Determination of Serum Iron
Abstract
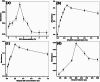
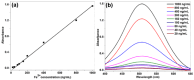
A facile, selective and sensitive method was devised for the Fe3+ quantification in low volume samples, such as bovine serum based on suspended droplet microextraction (SDME). Various process parameters such as concentrations of acid (1.5% hydrochloric acid), complexing agent (0.7% ammonium thiocyanate), quaternary ammonium salt (0.2% Aliquat 336) and extracting solvent (500 µL octanol) were optimised. Ammonium thiocyanate forms water soluble, red coloured, anionic ferric thiocyanate complex [Fe(SCN)6]3- with Fe3+ ions released from the iron-protein complex under an acidic medium. Negatively charged [Fe(SCN)6]3- complex forms hydrophobic ion associate Fe(SCN)6 3--Aliquat 3363 3+ with hydrophilic NH4 + head groups of Aliquat 336 and drives out the formed micelle from aqueous solution along with the iron complex. After stirring, ion associate bonded micelles are separated into a hanging micro droplet of octanol. Red coloured ferric thiocyanate complex in a suspended droplet is solubilised in methanol and Fe3+ concentration in serum samples is obtained by recording the spectrophotometric absorbance at 505 nm. The recoveries ranged from 96.2%-98.8% with relative standard deviation (RSD) (%) values from 1.4% to 5.0% at 100-400 ng/mL confirming interference free quantification at optimised conditions. The developed method was linear over the range of 20-1000 ng/mL of Fe3+ with a limit of detection of 2.4 ng/mL for the serum matrix. The developed method is applied to various bovine serum samples and Fe3+ concentration values ranged from 62.7 to 1582.5 ng/mL. The obtained values were in accordance with the results obtained from the electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry at 99% confidence level using t-test indicating the accuracy of the developed method. The proposed procedure offers various advantages such as enhanced sensitivity of the spectrophotometer towards iron determination, low-cost complexing agent, low sample volume, metal and biological interference free, simplicity and selectivity. Thus, the developed method can be an alternative to the routine spectrophotometric analysis of low volume samples such as serum and other biological fluids.
Keywords: ET‐AAS; colorimetric; complexing agent; iron; serum; spectrophotometric; suspended droplet microextraction.
© 2025 The Author(s). Analytical Science Advances published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: ultra trace determination of cadmium in water samples.Anal Chim Acta. 2007 Mar 7;585(2):305-11. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.01.007. Epub 2007 Jan 13. Anal Chim Acta. 2007. PMID: 17386679
-
Iron species determination by task-specific ionic liquid-based in situ solvent formation dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry.J Sci Food Agric. 2017 Oct;97(13):4635-4642. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8335. Epub 2017 May 19. J Sci Food Agric. 2017. PMID: 28369892
-
Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of Fe(III) and Al(III) using orthogonal signal correction-partial least squares calibration method after solidified floating organic drop microextraction.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015 Jan 25;135:929-34. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015. PMID: 25168229
-
Spectrophotometric method for quantitative determination of iron (III) from iron polymaltose complex in pharmaceutical formulations.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2006 Oct;19(4):299-303. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2006. PMID: 17105708
-
Green aspects, developments and perspectives of liquid phase microextraction techniques.Talanta. 2014 Feb;119:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.10.050. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24401382 Review.
References
-
- Rybkowska N., Strzelak K., and Koncki R., “A Comparison of Photometric Methods for Serum Iron Determination Under Flow Analysis Conditions,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 254 (2018): 307–313, 10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.059. - DOI
-
- Sherwood R. A, “Haemoglobins (Hemoglobins),” in Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 2nd ed., ed. Worsfold P., Townshend A., and Poole C (Elsevier, 2005), 223–229.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
