Adoption challenges to artificial intelligence literacy in public healthcare: an evidence based study in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 40371275
- PMCID: PMC12076014
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1558772
Adoption challenges to artificial intelligence literacy in public healthcare: an evidence based study in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
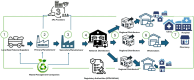
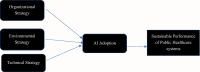
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming healthcare systems globally and improved the efficiency of its delivery. Countries like Saudi Arabia are facing unique adoption challenges in their public healthcare, these challenges are specific to AI literacy, understanding and effective usage of AI technologies. In addition, cultural, regulatory and operational barriers increase the complication of integrating AI literacy into public healthcare operations. In spite of its critical contribution in enabling sustainable healthcare development, limited studies have addressed these adoption challenges. Our study explores the AI literacy adoption barriers in context to Saudi Arabian public healthcare sector, focusing on its relevance for advancing healthcare operations and achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The research aims to identifying and addressing the adoption challenges of Artificial Intelligence literacy within the public healthcare in Saudi Arabia. The research aims to enhance the understanding of AI literacy, its necessity for enhancing healthcare operations, and the specific hurdles that impede its successful AI adoption in Saudi Arabia's public healthcare ecosystem. The research employs a qualitative analysis using the T-O-E framework to explore the adoption challenges of AI literacy. Additionally, the Best-Worse Method (BWM) is applied to evaluate the adoption challenges to AI literacy adoption across various operational levels within Saudi Arabia's public healthcare supply chain. The study uncovers substantial adoption challenges at operational, tactical, and strategic level, including institutional readiness, data privacy, and compliance with regulatory frameworks. These challenges complicate the adoption of AI literacy in the Saudi public healthcare supply chains. The research offers critical insights into the various issues affecting the promotion of AI literacy in Saudi Arabia's public healthcare sector. This evidence-based study provides essential commendations for healthcare professionals and policymakers to effectively address the identified challenges, nurturing an environment beneficial to the integration of AI literacy and advancing the goals of sustainable healthcare development.
Keywords: AI literacy; Saudi Arabia; Sustainable Development Goals; adoption challenges; artificial intelligence; public healthcare.
Copyright © 2025 Kumar, Singh, Kassar, Humaida, Joshi and Sharma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advancing Health Through Sustainable Development Goals-Saudi Arabia's Mid-Journey Progress and Insights.J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025 Mar 24;15(1):48. doi: 10.1007/s44197-025-00385-y. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40126702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Landscape of Artificial Intelligence in Saudi Arabia's Healthcare Sector: Current Trends and Challenges.Cureus. 2025 May 15;17(5):e84163. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84163. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40525046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of an artificial intelligence-driven operational management system on operational efficiency in health care organization in Saudi Arabia: a mediating role of staff attitude.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 30;13:1558644. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1558644. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40371290 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and strategies for wide-scale artificial intelligence (AI) deployment in healthcare practices: A perspective for healthcare organizations.Artif Intell Med. 2024 May;151:102861. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2024.102861. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Artif Intell Med. 2024. PMID: 38555850
-
Understanding the integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare organisations and systems through the NASSS framework: a qualitative study in a leading Canadian academic centre.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Jun 3;24(1):701. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11112-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38831298 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical