Impact of an artificial intelligence-driven operational management system on operational efficiency in health care organization in Saudi Arabia: a mediating role of staff attitude
- PMID: 40371290
- PMCID: PMC12075226
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1558644
Impact of an artificial intelligence-driven operational management system on operational efficiency in health care organization in Saudi Arabia: a mediating role of staff attitude
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming healthcare systems globally and improved the operational efficiency in healthcare organizations. The authors examined how an artificial intelligence (AI)-driven operational management system (OMS) affected operational efficiency in health care units in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). They also investigated the mediating role of staff attitudes in the relationship between OMSs and operational efficiency. This research contributes to the field by applying the theory of planned behavior to examine health care professionals' perceptions of AI-based OMSs and their impact on operational efficiency.
Methods: To achieve study objectives, a quantitative research design, with cross-sectional survey methodology, was used to gather data from 287 health care professionals across various hospitals in the KSA. The authors used a partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) approach to hypothesis testing.
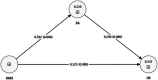
Results: The findings indicated that an AI-based OMS significantly improved operational efficiency and positively affected staff attitudes. Furthermore, staff attitudes mediated the relationship between an AI-based OMS and operational efficiency.
Discussion: The study finding highlights the dual benefits of AI-based OMSs in enhancing both operational performance and employee satisfaction. The results suggest that health care organizations in the KSA should invest in AI technologies to optimize operational efficiency and improve staff attitudes. The findings also emphasize the need to address employee perceptions to fully capitalize on the benefits of AI implementations. They also introduce staff attitudes as a mediating factor, offering new insights into the interaction between technology and employee engagement.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; artificial intelligence; health care; operational efficiency; operational management system; staff attitude.
Copyright © 2025 Kumar, Singh, Ahmed Kassar, Humaida, Joshi and Sharma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adoption challenges to artificial intelligence literacy in public healthcare: an evidence based study in Saudi Arabia.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 30;13:1558772. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1558772. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40371275 Free PMC article.
-
Patients' Attitudes Toward the Use of Artificial Intelligence as a Diagnostic Tool in Radiology in Saudi Arabia: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Hum Factors. 2024 Aug 7;11:e53108. doi: 10.2196/53108. JMIR Hum Factors. 2024. PMID: 39110973 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the future: perspectives on the Integration of Artificial Intelligence in health profession education: a multi-country survey.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Oct 18;24(1):1166. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06076-9. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39425151 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world application, challenges and implication of artificial intelligence in healthcare: an essay.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 Sep 2;43:3. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.43.3.33384. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 36284890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in nursing: an integrative review of clinical and operational impacts.Front Digit Health. 2025 Mar 7;7:1552372. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1552372. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40124108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Minor JS. Reengineering: the AI generation? Billions on the table In: Artificial intelligence and automation ed. Bourbakis NG. UK.: World Scientific; (1998). 96–142.
-
- Alshuwaikhat HM, Mohammed I. Sustainability matters in National Development Visions—Evidence from Saudi Arabia’s vision for 2030. Sustain. (2017). 9:408. doi: 10.3390/su9030408 - DOI
-
- Madkhali A, Sithole STM. Exploring the role of information Technology in Supporting Sustainability Efforts in Saudi Arabia. Sustain. (2023) 15:12375. doi: 10.3390/su151612375 - DOI
-
- Aminizadeh S, Heidari A, Dehghan M, Toumaj S, Rezaei M, Jafari Navimipour N, et al. . Opportunities and challenges of artificial intelligence and distributed systems to improve the quality of healthcare service. Artif Intell Med. (2024) 149:102779. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2024.102779, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tyagi AK, Fernandez TF, Mishra S, Kumari S. Intelligent automation Systems at the Core of industry 4.0 In: Abraham A, Piuri V, Gandhi N, Siarry P, Kaklauskas A, Madureira A, editors. Intelligent systems design and applications. Cham: Springer International Publishing; (2021). 1–18.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical