Health-state utility values and their time to deterioration in informal caregivers of older patients with chronic diseases
- PMID: 40371298
- PMCID: PMC12074913
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1531608
Health-state utility values and their time to deterioration in informal caregivers of older patients with chronic diseases
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to assess health state utility values (HSUVs) in caregivers of older patients with chronic diseases receiving or not receiving social worker support.
Methods: This multicentric open-label randomized study assigned caregivers to receive either an informational booklet alone or one accompanied by social worker support. Caregivers completed EQ-5D-3L each semester for 24 months. We reported caregiver HSUVs at baseline and after 6, 12, 18, and 24 months using EQ-5D-3L utility index scores and exploring their time to deterioration (TTD).
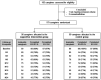
Results: Among 179 included caregivers, the percentage reporting some or extreme problems on five EQ-5D-3L dimensions remained almost stable over time with a median EQ-5D-3L utility index score of 0.89 [0.80-1.00] at baseline (n = 177), 0.80 [0.80-0.89] at M6 (n = 125), and 0.80 [0.73-0.91] at M24 (n = 81). Among the respondents, 62% (n = 109) experienced a deterioration in EQ-5D-3L utility index score, with a median TTD of 9.1 months [95%CI 6.2-14.9] in the control group (CG) and 9.5 months [6.3-14.4] in the supportive intervention group (SIG) (HR = 1.06 [0.73-1.54]), p-value = 0.76.
Conclusion: Our study provides a catalog of HSUVs across different caregiver profiles and at various follow-up time points, which can inform future economic evaluations.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02626377.
Keywords: caregiver; economic value; health-state utility value; older patient; social worker support; time to deterioration.
Copyright © 2025 Pozet, Falcoz, Roller, Jai, Meurisse and Nerich.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schofield D, Shrestha RN, Zeppel MJB, Cunich MM, Tanton R, Veerman JL, et al. . Economic costs of informal care for people with chronic diseases in the community: lost income, extra welfare payments, and reduced taxes in Australia in 2015-2030. Health Soc Care Community. (2019) 27:493–501. doi: 10.1111/hsc.12670, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- BVA, Fondation April. BVA Xsight . (2022). Baromètre des aidants – Avancées et perspectives. Available online at: https://www.bva-xsight.com/sondages/barometre-aidants-bva-fondation-apri...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

