Advancing precision oncology with AI-powered genomic analysis
- PMID: 40371349
- PMCID: PMC12075946
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1591696
Advancing precision oncology with AI-powered genomic analysis
Abstract
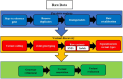
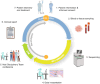
Multiomics data integration approaches offer a comprehensive functional understanding of biological systems, with significant applications in disease therapeutics. However, the quantitative integration of multiomics data presents a complex challenge, requiring highly specialized computational methods. By providing deep insights into disease-associated molecular mechanisms, multiomics facilitates precision medicine by accounting for individual omics profiles, enabling early disease detection and prevention, aiding biomarker discovery for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment monitoring, and identifying molecular targets for innovative drug development or the repurposing of existing therapies. AI-driven bioinformatics plays a crucial role in multiomics by computing scores to prioritize available drugs, assisting clinicians in selecting optimal treatments. This review will explain the potential of AI and multiomics data integration for disease understanding and therapeutics. It highlight the challenges in quantitative integration of diverse omics data and clinical workflows involving AI in cancer genomics, addressing the ethical and privacy concerns related to AI-driven applications in oncology. The scope of this text is broad yet focused, providing readers with a comprehensive overview of how AI-powered bioinformatics and integrative multiomics approaches are transforming precision oncology. Understanding bioinformatics in Genomics, it explore the integrative multiomics strategies for drug selection, genome profiling and tumor clonality analysis with clinical application of drug prioritization tools, addressing the technical, ethical, and practical hurdles in deploying AI-driven genomics tools.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; bioinformatics; genomics; precision oncology; therapeutics and analysis resource.
Copyright © 2025 Srivastava.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence and the impact of multiomics on the reporting of case reports.World J Clin Cases. 2025 May 26;13(15):101188. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i15.101188. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 40420936 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Reimagined: CRISPR and Multiomics Transform Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Diagnosis and Therapy.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Apr;28(4):e70189. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70189. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 40269480 Review.
-
New horizons at the interface of artificial intelligence and translational cancer research.Cancer Cell. 2025 Apr 14;43(4):708-727. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2025.03.018. Cancer Cell. 2025. PMID: 40233719 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Precision Medicine: Multi-Omics and Spatial Multi-Omics Approaches in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL).Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Nov 28;29(12):404. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2912404. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 39735973 Review.
-
Precision medicine in colorectal cancer: Leveraging multi-omics, spatial omics, and artificial intelligence.Clin Chim Acta. 2024 Jun 1;559:119686. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.119686. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38663471 Review.
Cited by
-
[Racial differences in treatment and prognosis of gastric signet ring cell carcinoma: analysis based on SEER and TCGA databases].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Aug 20;45(8):1706-1717. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.15. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40916532 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Adams R., Steckel M., Nicke B., Pohlenz H.-D. (2016). RNAi as a tool for target discovery in early pharmaceutical research. Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 71, 35–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

