Molecular pharmacokinetic mechanism of JBP485 against aristolochic acid I (AAI) -induced nephrotoxicity
- PMID: 40371353
- PMCID: PMC12074917
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1577942
Molecular pharmacokinetic mechanism of JBP485 against aristolochic acid I (AAI) -induced nephrotoxicity
Abstract
Introduction: In this study, we investigated the protective effect of JBP485 against aristolochic acid I (AAI)-induced nephrotoxicity and explored the pharmacokinetic mechanisms. The effects of JBP485 on AAI-induced cytotoxicity and nephrotoxicity were evaluated in vitro and in vivo, respectively.
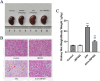
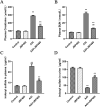
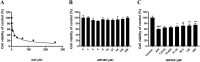
Methods: To ascertain the protective effect of JBP485 against AAI-induced nephrotoxicity, we measured levels of urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (CRE), and indoxol sulfate in blood and urine; determined kidney weight-to-body weight ratio; and performed hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Cell viability and Western blotting assays, along with determination of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) contents, were carried out to explore mechanisms underlying the protective effects of JBP485 against AAI-induced nephrotoxicity.
Results: JBP485 treatment attenuated AAI-induced injuries in rat kidney while decreasing the levels of indoxyl sulfate, CRE, and BUN in plasma and increasing those of indoxyl sulfate in urine compared to that in AAI alone-treated group. The co-administration of JBP485 with AAI significantly increased the concentration and AUC of AAI in plasma, while decreasing its cumulative urinary excretion and renal clearance. Moreover, JBP485 reduced the uptake of AAI in kidney slices and human organic anion transporter 1/3 (hOAT1/3)-transfected human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells, suggesting that JBP485 ameliorated AAI-induced nephrotoxicity by reducing renal exposure to AAI via OAT inhibition. Meanwhile, JBP485 modulated the abnormal expressions of Oat1, Oat3, organic cation transporter 2 (Oct2), P-glycoprotein (P-gp), multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (Mrp2) and multidrug and toxin extrusion proteins 1 (Mate 1) in rat kidney, suggesting that JBP485 improved tubular secretion in AAI-treated rats. Moreover, JBP485 reversed the AAI-induced changes in the expression of heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), NAD(P) H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein expressions and Bcl-2-like protein 4 (Bax) induced by AAI in rat kidney. JBP485 increased cell viability and reduced intracellular levels of ROS in NRK-52E cells treated with AAI.
Discussion: These results suggested that JBP485 protected against AAI-induced renal oxidative stress. All results indicated that JBP485 protected against AAI-induced nephrotoxicity by reducing renal exposure to AAI and alleviating oxidative stress. Our findings suggested that JBP485 has potential as a renoprotective agent for the prevention of AAI-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: DDI; JBP485; OATs; aristolochic acid I; nephrotoxicity.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Jin, Wang, Wu, Meng, Zhong, Sun, Wei, Gao, Kaku, Huo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author TK was employed by Japan Bioproducts Industry Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


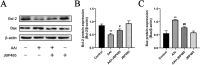



References
-
- Aigbe F. R., Sofidiya O. M., James A. B., Sowemimo A. A., Akindere O. K., Aliu M. O., et al. (2019). Evaluation of the toxicity potential of acute and sub-acute exposure to the aqueous root extract of Aristolochia ringens Vahl. (Aristolochiaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 244, 112150. 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112150 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

