Insights from a Long-Term Outdoor Mesocosm Study: eDNA Metabarcoding Reveals Exacerbated but Transient Impacts from a Nanoenabled Pesticide Formulation (Nano-TiO2-Coated Carbendazim) on Freshwater Microbial Communities
- PMID: 40371373
- PMCID: PMC12070410
- DOI: 10.1021/acsestwater.5c00014
Insights from a Long-Term Outdoor Mesocosm Study: eDNA Metabarcoding Reveals Exacerbated but Transient Impacts from a Nanoenabled Pesticide Formulation (Nano-TiO2-Coated Carbendazim) on Freshwater Microbial Communities
Abstract
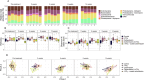
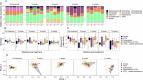
Fungicides currently encompass the second-most-used class of agricultural pesticides globally. Residues are frequently detected in freshwater, leading to undesired ecological impacts. Nanoenabled pesticide formulations have recently gained prominence in the scientific literature and have been suggested to exhibit favorable properties over conventional pesticide formulations by facilitating reductions in emissions toward nontarget locations. However, data on unintended effects on nontarget aquatic communities are scarce, especially concerning microbial communities. In this study, long-term effects of nano titanium-dioxide- (nTiO2)-coated carbendazim and its constituents on (pelagic) freshwater microbial communities in simulated agricultural ditches were investigated over a period of 14 weeks using environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding. Impacts on bacterial diversity (α and β) were observed 2 weeks after the treatment application and most pronounced in the nTiO2-coated carbendazim treatment, followed by its active substance, i.e., noncoated carbendazim. The observed patterns possibly imply that nTiO2-coated carbendazim imposed more pronounced and potentially delayed or extended effects compared to the noncoated form of carbendazim. Bacterial communities also proved to be resilient under the tested conditions as they returned to the control-state within 5 weeks after the treatment application. Overall, our data suggest that eDNA metabarcoding data on microbial communities can help uncover time-dependent effects of nanoformulated pesticides.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impacts of a novel controlled-release TiO2-coated (nano-) formulation of carbendazim and its constituents on freshwater macroinvertebrate communities.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Sep 10;838(Pt 4):156554. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156554. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35691359
-
Zooplankton community turnover in response to a novel TiO2-coated nano-formulation of carbendazim and its constituents.Environ Pollut. 2023 Sep 15;333:121894. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121894. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 37271364
-
Heatwaves, elevated temperatures, and a pesticide cause interactive effects on multi-trophic levels of a freshwater ecosystem.Environ Pollut. 2023 Jun 15;327:121498. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121498. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 36965684
-
Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Current applications and future prospects for freshwater fish monitoring.J Environ Manage. 2025 Mar;376:124531. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.124531. Epub 2025 Feb 16. J Environ Manage. 2025. PMID: 39955904 Review.
-
Environmental DNA metabarcoding for benthic monitoring: A review of sediment sampling and DNA extraction methods.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Apr 20;818:151783. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151783. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34801504 Review.
References
-
- de Souza R. M.; et al. Occurrence, impacts and general aspects of pesticides in surface water: A review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. 10.1016/j.psep.2019.12.035. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
