A Dual-Sequence MRI-Based Radiomics Model for Predicting High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation Efficacy in Adenomyosis Treatment
- PMID: 40371382
- PMCID: PMC12075450
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S512216
A Dual-Sequence MRI-Based Radiomics Model for Predicting High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Ablation Efficacy in Adenomyosis Treatment
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study is to develop a predictive model for the therapeutic efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation in the treatment of adenomyosis, utilizing dual-sequence MRI radiomics.
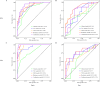
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 114 patients diagnosed with adenomyosis who underwent ultrasound-guided HIFU ablation under conscious sedation between July 2021 and July 2023. Patients were randomly allocated into a training set and a test set at a ratio of 7:3. The study aimed to evaluate the distribution of clinical characteristics among patients experiencing effective versus ineffective ablation at two distinct classification thresholds (0.7 and 0.5). Multiple models were developed to explore the combination of effective radiomic features derived from dual-sequence MRI and clinical data. Radiomic features were extracted from the MRI images of adenomyosis lesions in the training set. This process included feature extraction, selection, model construction, and evaluation. Logistic regression was used to construct the predictive model, and its performance was assessed on the test set using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The Delong test, net reclassification improvement (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) were used to compare the predictive accuracy of the models.
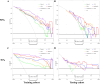
Results: The predictive model showed better alignment with actual ablation outcomes, particularly for predicting ablation success rates exceeding 50%. The combination of radiomic features from the two MRI sequences achieved an AUC of 0.84 in the test set. Decision curve analysis demonstrated that the combined model provided greater net benefit than the single-sequence radiomics model across a broader range of risk thresholds. For the prediction of 70% efficacy, the combined model achieved an AUC of 0.804 in the test set, slightly lower the 50% efficacy prediction task.
Conclusion: The model, based on dual-sequence MRI radiomics, emerges as a promising tool for predicting the efficacy of HIFU ablation, potentially aiding clinicians in anticipating the outcomes of HIFU ablation procedures.
Keywords: ablation; adenomyosis; high-intensity focused ultrasound; magnetic resonance imaging; radiomics analysis.
© 2025 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors affirm that there were no financial or commercial ties that might be viewed as having a potential conflict of interest for this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prediction of clinical outcome for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of adenomyosis based on non-enhanced MRI radiomics.Int J Hyperthermia. 2025 Dec;42(1):2468766. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2025.2468766. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Int J Hyperthermia. 2025. PMID: 39988330
-
Development and validation of a radiomics model based on T2-weighted imaging for predicting the efficacy of high intensity focused ultrasound ablation in uterine fibroids.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Feb 1;14(2):1803-1819. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-916. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38415139 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a combined model based on dual-sequence MRI radiomics for predicting the efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for hysteromyoma.Int J Hyperthermia. 2023;40(1):2149862. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2149862. Int J Hyperthermia. 2023. PMID: 36535929
-
Prediction of Ablation Rate for High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Therapy of Adenomyosis in MR Images Based on Multi-model Fusion.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Aug;37(4):1579-1590. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01063-4. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38441701 Free PMC article.
-
High intensity focused ultrasound for the treatment of adenomyosis: selection criteria, efficacy, safety and fertility.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017 Jun;96(6):707-714. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13159. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2017. PMID: 28437003 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

