Oxidative cell death in the central nervous system: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 40371389
- PMCID: PMC12075549
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1562344
Oxidative cell death in the central nervous system: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Abstract
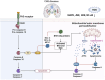
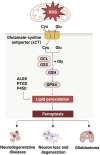
Oxidative cell death is caused by an overproduction of reactive oxygen species and an imbalance in the antioxidant defense system, leading to neuronal dysfunction and death. The harm of oxidative stress in the central nervous system (CNS) is extensive and complex, involving a variety of molecular and cellular level changes that may lead to a variety of acute and chronic brain pathologies, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases and psychological disorders. This review provides an in-depth look at the mechanisms of oxidative cell death in the central nervous system diseases. In addition, the review evaluated existing treatment strategies, including antioxidant therapy, gene therapy, and pharmacological interventions targeting specific signaling pathways, all aimed at alleviating oxidative stress and protecting nerve cells. We also discuss current advances and challenges in clinical trials, and suggest new directions for future research, including biomarker discovery, identification of potential drug targets, and exploration of new therapeutic techniques, with a view to providing more effective strategies for the treatment of CNS diseases.
Keywords: antioxidant therapy; central nervous system; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroprotection; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Liu, Wang, Feng, Piao and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Antioxidant therapy in acute central nervous system injury: current state.Pharmacol Rev. 2002 Jun;54(2):271-84. doi: 10.1124/pr.54.2.271. Pharmacol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12037143 Review.
-
Transcriptional activation of antioxidant gene expression by Nrf2 protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal death associated with acute and chronic neurodegeneration.Exp Neurol. 2020 Jun;328:113247. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113247. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32061629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupeol Treatment Attenuates Activation of Glial Cells and Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Neuropathology in Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 29;23(11):6086. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116086. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682768 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Antioxidants in Modulating the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Their Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 12;26(8):3658. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083658. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights into 4-Aminopyridine-Induced Cell Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 12;26(16):7768. doi: 10.3390/ijms26167768. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40869089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awad S. M., Attia Y. A., ElSayed H., Abdelhafez S. H., Keshta A. T., Rashad E., et al. (2025). Efficacy of curcumin-selenium nanoemulsion in alleviating oxidative damage induced by aluminum chloride in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Histol. 56, 122. 10.1007/s10735-025-10406-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

