Immunotherapy of endometrial cancer via CD47 blockade-mediated macrophage phagocytosis
- PMID: 40371397
- PMCID: PMC12077145
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf143
Immunotherapy of endometrial cancer via CD47 blockade-mediated macrophage phagocytosis
Abstract
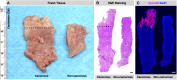
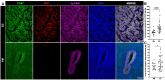
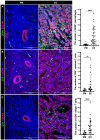
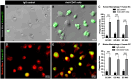
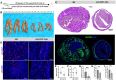
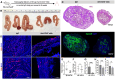
The interaction between CD47 expressed on cancer cells and signal regulatory protein-α located on macrophages blocks the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages. Our data reveal that human endometrial cancer cells (hECCs) upregulate the CD47 level on their surface and that there is a high density of tumor-associated macrophages within the microenvironment of human endometrial cancer. In vitro functional assay shows that an anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody (mAb) promotes the phagocytosis of hECCs by macrophages. Systemic and in situ treatments with an anti-CD47 mAb effectively reduce tumor burden in vivo in a genetically engineered mouse model of endometrial cancer. Thus, this study provides preclinical evidence that CD47 blockade using an anti-CD47 mAb to augment macrophage phagocytosis is a potential therapeutic strategy for endometrial cancer.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; CD47; Medical Sciences; endometrial cancer; immunotherapy; macrophage; phagocytosis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP. 1996. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science. 271(5256):1734–1736. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

