Aging in Southeast Asia and Japan: Challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 40371612
- PMCID: PMC12238812
- DOI: 10.1111/ggi.70062
Aging in Southeast Asia and Japan: Challenges and opportunities
Abstract
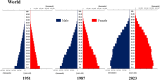
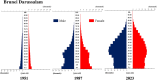
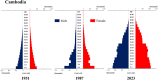
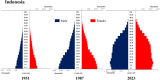
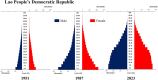
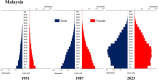
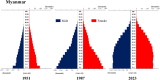
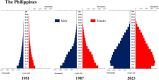
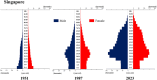
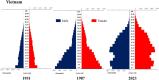
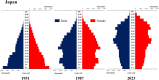
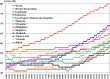
Trends in life expectancy and fertility in Southeast Asia reflect the region's vulnerability to conflicts, natural disasters, infectious diseases and other crises. Southeast Asia is characterized by significant diversity, not only in its natural environment, history, religions, economic situations and political systems, but also in its challenges and healthcare systems, which include traditional medicine and local healing practices. Despite these differences, common issues are shared across the region, such as an aging population, the need for universal access to safe and secure healthcare, and the pursuit of peace and environmental harmony. Currently, Japan's aging population is more pronounced than in Southeast Asia, with a notable prevalence of older adults with chronic diseases, including dementia and living alone. However, if current demographic trends continue, most Southeast Asian nations might face similar challenges in the future. This article focuses on the 90th percentile age over time and advocates the importance of considering the relative position of age in society, rather than simply focusing on age alone. Additionally, it is recognized that individuals of the same chronological age can show significant variation in health, shaped by their life circumstances and lifestyles. As Japan leads in addressing aging-related issues, it plays a critical role in sharing its experiences. Because the health status of certain age groups in society varies from region to region and era to era, depending on the environment and culture, measures should be adapted to the realities of each society, with the cooperation of the international community to address shared challenges. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2025; 25: 837-854.
Keywords: 90th percentile age; Japan; Southeast Asia; aging; older adults.
© 2025 The Author(s). Geriatrics & Gerontology International published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Geriatrics Society.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Hail Lifestyle Medicine consensus position statement as a medical specialty: Middle Eastern perspective.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 20;13:1455871. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1455871. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40620567 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- United Nations . World Population Prospects 2024: Summary of Results. UN DESA/POP/2024/TR/NO. 9. New York: United Nations, 2024.
-
- Riley JC. Estimates of regional and global life expectancy, 1800‐2001. Popul Dev Rev 2005; 31: 537–543.
-
- Wolff JL, Starfield B, Anderson G. Prevalence, expenditures, and complications of multiple chronic conditions in the elderly. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 2269–2276. - PubMed
-
- Prince MJ, Wu F, Guo Y, Robledo LMG et al. The burden of disease in older people and implications for health policy and practice. Lancet 2015; 385: 549–562. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet 2024; 403: 2100–2132. 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00367-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

