Natural product sennoside B disrupts liquid-liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein by inhibiting its RNA-binding activity
- PMID: 40371698
- PMCID: PMC12082725
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2501743
Natural product sennoside B disrupts liquid-liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein by inhibiting its RNA-binding activity
Abstract
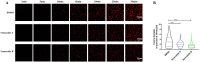
The nucleocapsid protein (NP) of SARS-CoV-2, an RNA-binding protein, is capable of undergoing liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) during viral infection, which plays a crucial role in virus assembly, replication, and immune regulation. In this study, we developed a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) method for identifying inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 NP-RNA interaction. Using this HTRF-based approach, we identified two natural products, sennoside A and sennoside B, as effective blockers of this interaction. Bio-layer interferometry assays confirmed that both sennosides directly bind to the NP, with binding sites located within the C-terminal domain. Additionally, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) experiments revealed that sennoside B significantly inhibited RNA-induced LLPS of the NP, while sennoside A displayed comparatively weaker activity. Thus, the developed HTRF-based assay is a valuable tool for identifying novel compounds that disrupt the RNA-binding activity and LLPS of the SARS-CoV-2 NP. Our findings may facilitate the development of antiviral drugs targeting SARS-CoV-2 NP.
Keywords: HTRF; SARS-CoV-2; liquid-liquid phase separation; nucleocapsid protein; sennoside B.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unveiling potential inhibitors targeting the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2: Structural insights into their binding sites.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jul;273(Pt 2):133167. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133167. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38885868
-
Targeting the liquid-liquid phase separation of nucleocapsid broadly inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 strains.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Apr 5;756:151594. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151594. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40086356
-
Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 phase separates into RNA-rich polymerase-containing condensates.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 27;11(1):6041. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19843-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33247108 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation of nucleocapsid proteins during SARS-CoV-2 and HIV-1 replication.Cell Rep. 2023 Jan 31;42(1):111968. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111968. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36640305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the role of the nucleocapsid protein in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: From viral life cycle to vaccine development.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 2):135201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135201. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39216563 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
