Development of 4T1 breast cancer mouse model system for preclinical carbonic anhydrase IX studies
- PMID: 40371725
- PMCID: PMC12319724
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.70052
Development of 4T1 breast cancer mouse model system for preclinical carbonic anhydrase IX studies
Abstract
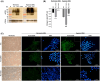
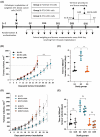
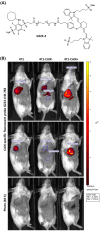
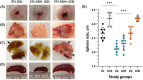
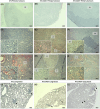
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive type of breast cancer, for which targeted treatment is currently lacking. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a known cancer target due to its selective overexpression in hypoxia, a hallmark of many solid cancers including TNBC. This study aimed to develop a robust murine TNBC cell line 4T1-based model system that could be used in the comprehensive preclinical evaluation of targeting CAIX. The model is based on the original 4T1 breast cancer cell line and two genetically edited versions of it-one with biallelic CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Car9 inactivation and another with constitutively expressed Car9, thus ensuring negative and positive controls for CAIX production in the model system, respectively. The generated cell lines were validated for CAIX production and characterised functionally in vitro and in vivo after orthotopic implantation in syngeneic BALB/c mice. Results demonstrated significantly reduced primary tumour growth and metastatic progression rates in animals with CAIX-deficient tumours, while the CAIX-expressing tumours had vascularised phenotypes with prominent central areas of coagulative necrosis. The differential CAIX expression levels in the model were preserved during tumour growth in syngeneic mice, as verified by in vivo imaging using a novel high-affinity CAIX-specific near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent imaging probe, GZ22-4. Constitutive overexpression of autologous CAIX did not elicit specific autoantibody responses in vivo, demonstrating the suitability of this model for evaluating the efficacy of anti-CAIX vaccination as a therapeutic strategy. The in vivo study was repeated as an independent experiment and demonstrated good robustness of the developed model.
Keywords: 4T1 model; breast cancer; cancer imaging; carbonic anhydrase IX; hypoxia; preclinical models.
© 2025 The Author(s). FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
DM, AZ, and EC declare that they have patent applications and patents on Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors, including GZ22‐4. The rest of the authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression and function of CAIX and CAXII in breast cancer: A comparison between tumorgraft models and cells.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 2;13(7):e0199476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199476. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29965974 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of virus-like particle Vaccine Against Carbonic Anhydrase IX Efficacy in a Mouse Breast Cancer Model System.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 May;66(5):1206-1219. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-01021-5. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38217826
-
CD24a knockout results in an enhanced macrophage- and CD8⁺ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immune responses in tumor microenvironment in a murine triple-negative breast cancer model.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Aug 9;32(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01165-3. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 40783744 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The relationship between carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) and patient survival in breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.Diagn Pathol. 2023 Apr 15;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01325-9. Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37061698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71, 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Hua Z, White J and Zhou J (2022) Cancer stem cells in TNBC. Semin Cancer Biol 82, 26–34. - PubMed
-
- Ivanova L, Zandberga E, Silina K, Kalnina Z, Abols A, Endzelins E, Vendina I, Romanchikova N, Hegmane A, Trapencieris P et al. (2015) Prognostic relevance of carbonic anhydrase IX expression is distinct in various subtypes of breast cancer and its silencing suppresses self‐renewal capacity of breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 235–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

