Chemically induced partial unfolding of the multifunctional apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1
- PMID: 40371780
- PMCID: PMC12079476
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.70148
Chemically induced partial unfolding of the multifunctional apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Chemically induced partial unfolding of the multifunctional apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1".Protein Sci. 2025 Oct;34(10):e70222. doi: 10.1002/pro.70222. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40980952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
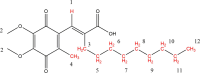
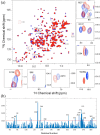
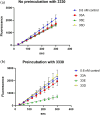
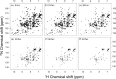
Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease I (APE1) acts as both an endonuclease and a redox factor to ensure cell survival. The two activities require different conformations of APE1. As an endonuclease, APE1 is fully folded. As a redox factor, APE1 must be partially unfolded to expose the buried residue Cys65, which reduces transcription factors including AP-1, NF-κB, and HIF-1α and thereby enables them to bind DNA. To determine a molecular basis for partial unfolding associated with APE1's redox activity, we characterized specific interactions of a known redox inhibitor APX3330 with APE1 through waterLOGSY and 1H-15N HSQC NMR approaches using ethanol and acetonitrile as co-solvents. We find that APX3330 binds to the endonuclease active site in both co-solvents and to a distant small pocket in acetonitrile. Prolonged exposure of APE1 with APX3330 in acetonitrile resulted in a time-dependent loss of 1H-15N HSQC chemical shifts (~35%), consistent with partial unfolding. Regions that are partially unfolded include adjacent N- and C-terminal beta strands within one of the two sheets comprising the core, which converge within the small binding pocket defined by the CSPs. Removal of APX3330 via dialysis resulted in a slow reappearance of the 1H-15N HSQC chemical shifts suggesting that the effect of APX3330 is reversible. APX3330 significantly decreases the melting temperature of APE1 but has no effect on endonuclease activity using a standard assay in either co-solvent. Our results provide insights on reversible partial unfolding of APE1 relevant for its redox function as well as the mechanism of redox inhibition by APX3330.
Keywords: APE1; APX3330; HSQC NMR; partial unfolding.
© 2025 The Author(s). Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
MRK is the CSO and cofounder of Apexian Pharmaceuticals, which developed APX3330 for an oncology clinical trial and Ocuphire Pharma (now Opus Genetics) for a diabetic retinopathy clinical trial. Neither Apexian Pharmaceuticals nor Opus Genetics had any input or control over the contents of this manuscript.
Figures





Update of
-
Chemically induced partial unfolding of the multifunctional Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 26:2023.06.29.547112. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.29.547112. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Protein Sci. 2025 Jun;34(6):e70148. doi: 10.1002/pro.70148. PMID: 37425839 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Barchiesi A, Bazzani V, Jabczynska A, Borowski LS, Oeljeklaus S, Warscheid B, et al. DNA repair protein APE1 degrades dysfunctional abasic mRNA in mitochondria affecting oxidative phosphorylation. J Mol Biol. 2021;433:167125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

