Assessing the safety of microbiome perturbations
- PMID: 40371892
- PMCID: PMC12282321
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.001405
Assessing the safety of microbiome perturbations
Abstract
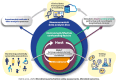
Everyday actions such as eating, tooth brushing or applying cosmetics inherently modulate our microbiome. Advances in sequencing technologies now facilitate detailed microbial profiling, driving intentional microbiome-targeted product development. Inspired by an academic-industry workshop held in January 2024, this review explores the oral, skin and gut microbiomes, focussing on the potential long-term implications of perturbations. Key challenges in microbiome safety assessment include confounding factors (ecological variability, host influences and external conditions like geography and diet) and biases from experimental measurements and bioinformatics analyses. The taxonomic composition of the microbiome has been associated with both health and disease, and perturbations like regular disruption of the dental biofilm are essential for preventing caries and inflammatory gum disease. However, further research is required to understand the potential long-term impacts of microbiome disturbances, particularly in vulnerable populations including infants. We propose that emerging technologies, such as omics technologies to characterize microbiome functions rather than taxa, leveraging artificial intelligence to interpret clinical study data and in vitro models to characterize and measure host-microbiome interaction endpoints, could all enhance the risk assessments. The workshop emphasized the importance of detailed documentation, transparency and openness in computational models to reduce uncertainties. Harmonisation of methods could help bridge regulatory gaps and streamline safety assessments but should remain flexible enough to allow innovation and technological advancements. Continued scientific collaboration and public engagement are critical for long-term microbiome monitoring, which is essential to advancing safety assessments of microbiome perturbations.
Keywords: artificial intelligence (AI)/ML; clinical studies; gut; in vitro models; microbiome; oral; safety assessment; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M., A.A., B.M., and S.K. are Unilever employees. A.W.W. has received consultancy fees from EnteroBiotix Ltd and ZOE Ltd. G.A. is a Reckitt employee. A.S. is a BugBiome employee. A.J.M. has received travel, consultancy and speaker’s fees in the areas of microbial control, biofilms and the human microbiome and is a coinventor on a patent involving pro- and post-biotic bacteria. H.L.B. sits on the Scientific Advisory Board of Chuckling Goat Ltd. O.H. is an IFF Health and Biosciences employee. C.S. is a regulatory consultant. J.P.T. is an employee of The Procter and Gamble Company.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

