Mucinous cystic neoplasms and simple mucinous cysts are two distinct precursors of pancreatic cancer: clinicopathological, genomic, and transcriptomic characterization
- PMID: 40371932
- PMCID: PMC12256392
- DOI: 10.1002/path.6437
Mucinous cystic neoplasms and simple mucinous cysts are two distinct precursors of pancreatic cancer: clinicopathological, genomic, and transcriptomic characterization
Abstract
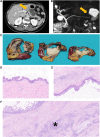
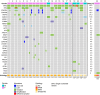
Mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs) of the pancreas are macroscopic precursors of pancreatic cancer. A similar cystic lesion but lacking the ovarian-type subepithelial stroma has been recently defined as a simple mucinous cyst (SMC); however, its nature remains unclear. This study aims to define the clinicopathological and molecular profiles of a cohort of MCNs and SMCs of the pancreas and their associated invasive carcinoma. Overall, 23 cases were identified, comprising 19 MCNs and 4 SMCs with co-occurring invasive carcinoma. A multiregional (two samples from each cystic lesion and one from the adenocarcinoma) DNA and RNA sequencing approach was used. The key findings can be summarized as follows: (1) Molecular association: In 22/23 cases (95.7%), the concomitant mucinous cyst and invasive carcinoma shared specific genomic alterations, establishing for the first time that SMC is a true precursor of pancreatic cancer. (2) Clinical behavior: carcinomas arising from SMC appeared to be more aggressive than those arising from MCN. (3) Mutational profile: both cyst types showed significant similarities to conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), with KRAS and TP53 the most commonly altered genes. (4) Intracystic heterogeneity: while most molecular alterations were present in both analyzed cystic areas, RNF43 showed the highest heterogeneity. (5) CDKN2A: its alterations were predominantly restricted to the invasive component, suggesting a role in driving the invasion in a subset of cases. CNKN2A may also serve as a potential biomarker for identifying high-risk cysts. (6) RNAseq: most cases showed a switch from the classical to the basal transcriptome subtype during the progression from cystic neoplasms to invasive cancers. These findings establish SMCs as new precursors of pancreatic cancer and provide critical insights into the tumorigenesis of MCNs, with potential immediate implications for tumor taxonomy and clinical management. © 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Keywords: CDKN2A; MCN; Mucinous cystic neoplasm; PDAC; RNF43; pancreatic precursors; simple mucinous cyst; transcriptome.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Journal of Pathology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2024; 74: 229–263. - PubMed
-
- Bizuayehu HM, Dadi AF, Ahmed KY, et al. Burden of 30 cancers among men: global statistics in 2022 and projections for 2050 using population‐based estimates. Cancer 2024; 130: 3708–3723. - PubMed
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . Digestive System Tumours (Vol. 1, 5th edn). International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, 2019.
-
- Singhi AD, Wood LD. Early detection of pancreatic cancer using DNA‐based molecular approaches. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021; 18: 457–468. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

