Targeting the Dependence on PIK3C3-mTORC1 Signaling in Dormancy-Prone Breast Cancer Cells Blunts Metastasis Initiation
- PMID: 40372253
- PMCID: PMC12167933
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2654
Targeting the Dependence on PIK3C3-mTORC1 Signaling in Dormancy-Prone Breast Cancer Cells Blunts Metastasis Initiation
Abstract
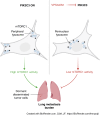
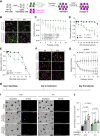
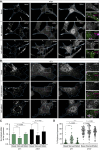
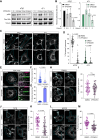
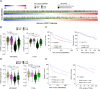
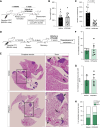
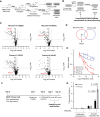
Halting breast cancer metastatic relapse following primary tumor removal remains challenging due to a lack of specific vulnerabilities to target during the clinical dormancy phase. To identify such vulnerabilities, we conducted genome-wide CRISPR screens on two breast cancer cell lines with distinct dormancy properties: 4T1 (short-term dormancy) and 4T07 (prolonged dormancy). The dormancy-prone 4T07 cells displayed a unique dependency on class III PI3K (PIK3C3). Unexpectedly, 4T07 cells exhibited higher mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity than 4T1 cells due to lysosome-dependent signaling occurring at the cell periphery. Pharmacologic inhibition of PIK3C3 suppressed this phenotype in the 4T1-4T07 models as well as in human breast cancer cell lines and a breast cancer patient-derived xenograft. Furthermore, inhibiting PIK3C3 selectively reduced metastasis burden in the 4T07 model and eliminated dormant cells in a HER2-dependent murine breast cancer dormancy model. These findings suggest that PIK3C3-peripheral lysosomal signaling to mTORC1 may represent a targetable axis for preventing dormant cancer cell-initiated metastasis in patients with breast cancer.
Significance: Dormancy-prone breast cancer cells depend on the class III PI3K to mediate peripheral lysosomal positioning and mTORC1 hyperactivity, which can be targeted to blunt breast cancer metastasis.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.L. Kleinman reports grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and other support from the Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé during the conduct of the study. A.P. Gomes reports other support from MetroBiotech outside the submitted work. J.A. Aguirre-Ghiso reports personal fees from the Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation and Astrin Biosciences and nonfinancial support from HiberCell LLC outside the submitted work and has a patent for WO2019191115A1/EP-3775171-B1 issued. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures


Update of
-
Targeting the dependence on PIK3C3-mTORC1 signaling in dormancy-prone breast cancer cells blunts metastasis initiation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 8:2023.08.02.551681. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.02.551681. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 16;85(12):2179-2198. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2654. PMID: 39211165 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- P30CA013330/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Miles for Moffit
- R01 CA292658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109182/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- The Gurwin Foundation
- Melanoma Research Alliance (MRA)
- Quebec Breast Cancer Foundation
- Samuel Waxman Cancer Research Foundation (SWCRF)
- CA253977/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Diane and Sal Guerrera Chair in Cancer Genetics
- U01 CA284085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RSG-22-164-01-MM/American Cancer Society (ACS)
- Institut de Recherche Clinique De Montréal Foundation
- Calcul Quebec
- CA284085/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- FDN-143281/Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)
- Fonds de Recherche du Québec - Santé (FRQS)
- CA109182/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Compute Canada (Calcul Canada)
- PJT-156086/Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)
- Canada Research Chairs (Chaires de recherche du Canada)
- 25244/Cancer Research Society (CRS)
- R01CA292658/National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Peter Quinlan Postdoctoral research Fellowship in Oncology
- R01 CA253977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- The Mark Foundation Aspire Program
- Rose C. Falkenstein Chair in Cancer Research
- Canadian Cancer Society (CCS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

