ARHGDIB as a prognostic biomarker and modulator of the immunosuppressive microenvironment in glioma
- PMID: 40372473
- PMCID: PMC12081808
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-025-04063-7
ARHGDIB as a prognostic biomarker and modulator of the immunosuppressive microenvironment in glioma
Abstract
Background: Glioma, a prevalent malignant intracranial tumor, exhibits limited therapeutic efficacy due to its immunosuppressive microenvironment, leading to a poor prognosis for patients. ARHGDIB is implicated in the remodeling of the tumor microenvironment and plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of various tumors. However, its regulatory effect within the immune microenvironment of glioma remains unclear.
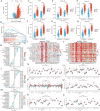
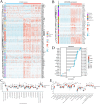
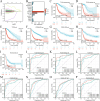
Methods: The mRNA expression pattern of ARHGDIB was analyzed using public databases, and its expression was further validated in our collected cohort through quantitative PCR (qPCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and LASSO-Cox regression were employed to ascertain the clinical significance of ARHGDIB in glioma. Subsequently, we systematically evaluated the association between ARHGDIB expression and immune characteristics within the glioma microenvironment, as well as its potential to predict treatment response in glioma. Additionally, in vitro experiments were conducted to elucidate the role of ARHGDIB in remodeling the glioma microenvironment and promoting tumor malignancy progression.
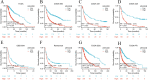
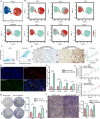
Results: Combined with bioinformatics analysis of public databases and validation with qPCR and IHC on our cohort, our findings indicate that ARHGDIB is markedly overexpressed in glioma and correlates with poor patient prognosis, thereby serving as a potential biomarker for adverse outcomes in glioma. Functional enrichment and immune infiltration analyses reveal that ARHGDIB is implicated in the recruitment of immunosuppressive cells, such as M2 macrophages and neutrophils, contributing to the alteration of the glioma immunosuppressive microenvironment and hindering the immune response. Further investigations through single-cell sequencing, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and in vitro experiments demonstrate that ARHGDIB exhibits an expression pattern akin to CD163, with its overexpression inducing M2 macrophage polarization and facilitating glioma cell proliferation and migration.
Conclusions: ARHGDIB emerges as a novel marker for tumor-associated macrophages, playing a crucial role in shaping the immunosuppressive microenvironment and representing a promising prognostic biomarker for glioma.
Keywords: ARHGDIB; Glioma; Immunosuppressive microenvironment; Prognosis; Tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be perceived as a potential conflict of interest. Ethical approval: All patients provided informed consent, and the ethics committee of XiangyaHospital, Central South University approved this study.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

