Three-dimensional reconstruction of gustatory papillae and its taste buds in short-hair cats (Felis Catus domestica, felidae, Carnivora)
- PMID: 40372507
- PMCID: PMC12081509
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-025-10764-2
Three-dimensional reconstruction of gustatory papillae and its taste buds in short-hair cats (Felis Catus domestica, felidae, Carnivora)
Abstract
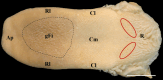
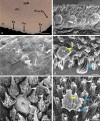
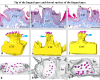
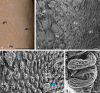
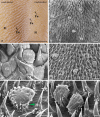
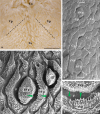
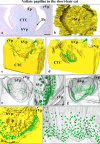
Previous studies on the cat's tongue focused on the anatomy of the tongue and on the lingual papillae micromorphology. According to new challenges in studies on gustatory papillae, we adopted a modern computer-aided method of 3D reconstruction of gustatory papillae from serial 2D cross-sections in the description of the taste bud system. The study in short-hair cats aimed for the first time in carnivores to analyze fungiform (Fu papillae) and vallate papillae (Vp papillae) with spatial visualization of connective tissue cores (CTCs) and the arrangement and exact number of taste buds (Tbs). Results indicate the diversity in size and internal connective tissue microstructure of Fu and Vp papillae in short-hair cats. Four types of CTCs were distinguished in Fu papillae: mushroom-like, club-like, columnar-like, and bud-like, whereas CTC in Vp papillae was mushroom-like. The Tbs of Fu and on Vp papillae were either evenly distributed or grouped. Tbs of Fu papillae analyzed in particular parts of the tongue and on Vp papillae revealed differences in its number. The estimated total number of Tbs on the tongue was up circa 8265. Our 2D and 3D Tbs analyses highlight the functional importance of different tongue regions: the lingual apex for food preselection, the lateral lingual surfaces for analyzing chewed food, and the caudal part of the tongue for final food tasting before swallowing. Comparing our results in cats with previous studies on herbivores, we recommend using proposed 3D analyses as effective tools for further comparative studies of mammalian gustatory structures.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction and modelling; Domestic Cat; Gustatory papillae; Taste buds.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: According to Polish law and the EU directive (no. 2010/63/EU), the studies conducted within the study do not require approval of the Local Ethical Committee for Experiments on Animals in Poznan. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The three-dimensional analysis of gustatory papillae and its taste buds on the tongue of the wild-living hare (Lepus europaeus), European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), and domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus f. domestica).Ann Anat. 2025 Jun;260:152667. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2025.152667. Epub 2025 May 1. Ann Anat. 2025. PMID: 40318704
-
Three-dimensional characteristic of fungiform papillae and its taste buds in European bison (Bison bonasus), cattle (Bos taurus), and Bison bonasus hybrid.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Jan 7;18(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-03111-5. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 34996440 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative study of fungiform papillae and taste buds on the cat's tongue.Anat Rec. 1990 Jan;226(1):108-11. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092260112. Anat Rec. 1990. PMID: 2297077
-
Spacing patterns on tongue surface-gustatory papilla.Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48(2-3):157-61. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.15272380. Int J Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15272380 Review.
-
Anterior and Posterior Tongue Regions and Taste Papillae: Distinct Roles and Regulatory Mechanisms with an Emphasis on Hedgehog Signaling and Antagonism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4833. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054833. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chamorro CA, Sandoval J, Fernandez JG, Fernandez M, de Paz P (1987) Compared studies of the lingual papillae of the cat (Felis catus) and the rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) by scanning electron microscopy. Anat Histol Embryol 16:37–47. 10.1111/j.1439-0264.1987.tb00722.x - PubMed
-
- Crouch JE (1969) Text-Atlas of Cat anatomy. LEA & FEBIGER, Philadelphia, pp 131–138
-
- Dyce KM, Sack WO, Wensing CJG (2010) Textbook of veterinary anatomy, 4th edn. SAUNDERS ELSEVIER, St. Louis, Missouri, pp 399–405
-
- Eizirik E, Murphy WJ (2009) Carnivores (Carnivora). In: Hedges SB, Kumar S (eds) Timetree of Life, Oxford University Press, pp 504–507
-
- Emura S (2018a) Morphology of the lingual papillae in the Asian golden Cat. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 95:19–22. 10.2535/ofaj.95.19 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

