High-dose vitamin C promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells by regulating the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway
- PMID: 40372538
- PMCID: PMC12081527
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-025-06211-z
High-dose vitamin C promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells by regulating the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction is closely associated with cancer development. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cells often exhibit altered energy metabolism, characterized by increased glycolysis and reduced oxidative phosphorylation. Enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and function may represent a promising therapeutic approach. High-dose vitamin C has demonstrated anti-tumor properties and the ability to reverse the Warburg effect, but its role in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and function remains unclear.
Methods: We evaluated the altered mitochondrial functional status of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells compared to FHC colorectal epithelial cells, assessed the effects of high-dose vitamin C on mitochondrial biogenesis and function in HCT116 cells, and explored the underlying regulatory mechanisms.
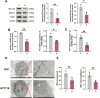
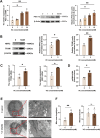
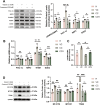
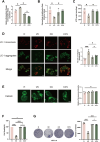
Results: HCT116 cells exhibited mitochondrial dysfunction compared to FHC cells, including decreased expression of electron transport chain complexes III and IV, reduced TFAM levels, and lower mtDNA content. Vitamin C treatment significantly enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis and function, as reflected by increased AMPK phosphorylation, upregulation of PGC-1α, SOD2, NRF2, TFAM, MT-CYB, and MTCO1, elevated mtDNA content, restored membrane potential, enhanced oxidative phosphorylation, and reduced glycolytic activity. Furthermore, vitamin C markedly suppressed HCT116 cell viability and clonogenic capacity, while these effects were substantially diminished by cotreatment with Compound C.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that high-dose vitamin C ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function in colorectal cancer cells through activation of the AMPK-PGC-1α signaling pathway, thereby suppressing tumor cell proliferation. These findings suggest that vitamin C may serve as a promising therapeutic agent for targeting mitochondrial metabolism in colorectal cancer.
Keywords: AMPK; Colorectal cancer; Mitochondrial biogenesis; PGC-1α; Vitamin C.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The diabetes medication canagliflozin promotes mitochondrial remodelling of adipocyte via the AMPK-Sirt1-Pgc-1α signalling pathway.Adipocyte. 2020 Dec;9(1):484-494. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2020.1807850. Adipocyte. 2020. PMID: 32835596 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis is impaired in osteoarthritis chondrocytes but reversible via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67(8):2141-53. doi: 10.1002/art.39182. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25940958 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the role of Dihuang Yinzi in regulating the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway to promote mitochondrial biogenesis and improve Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 2):118859. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118859. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39341266
-
Salicylates promote mitochondrial biogenesis by regulating the expression of PGC-1α in murine 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):436-441. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.074. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28712868
-
Globular CTRP3 promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in cardiomyocytes through AMPK/PGC-1α pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Jan;1861(1 Pt A):3085-3094. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.10.022. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27793739
References
-
- 2013 AMPK can suppress tumorigenesis and the Warburg effect. Cancer Discov, 3(3): OF15 - PubMed
-
- Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA (2019) Colorectal cancer. Lancet (London, England) 394(10207):1467–1480 - PubMed
-
- Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2008) Mitochondria in cancer cells: what is so special about them? Trends Cell Biol 18(4):165–173 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

