Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Conflict Management Perspectives Among Physician and Nurse Leaders
- PMID: 40372757
- PMCID: PMC12082374
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.9783
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Conflict Management Perspectives Among Physician and Nurse Leaders
Abstract
Importance: Decision-making conflict is common in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) and associated with negative outcomes for patients, families, and teams. Disparities in conflict outcomes are reported, yet no studies have explored conflict management approaches.
Objective: To understand approaches to conflict mediation and escalation in the PICU.
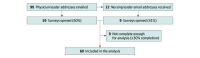
Design, setting, and participants: This national, multicenter, prospective, mixed-methods survey study recruited PICU physician and nursing directors from February to April 2023.
Exposure: PICU size, conflict policy, behavior contract tracking.
Main outcomes and measures: Closed- and open-ended survey questions were used to collect information on hospital policies, general conflict approaches, and specific approaches to scenarios.
Results: The overall response rate was 57% (68 of 120 surveys, with 60 complete enough for analysis). Overall, 30 of 51 respondents (59%) identified as female, with a wide distribution of reported years in current role and percentage of time spent in clinical care. Institution regions varied, with an even distribution among institutions with different PICU sizes. Conflict strategies were used variably across institutions. Approximately 65% (32 of 49) reported policies for conflict management. Only 23% (10 of 43) tracked conflicts and their outcomes. Few institutions trained staff in conflict management techniques. Compared with institutions that did not track behavior contracts, those that did were more likely to call ethics consults for conflict management (3 of 12 [25%] vs 0 of 20; P = .04) and to implement behavior contracts for more objective reasons (8 of 11 [73%] vs 4 of 16 [25%]; P = .02). Leaders offered ideas for multipronged conflict prevention and response based on strategies implemented at their institutions but also highlighted needs and concerns with existing approaches.
Conclusions and relevance: In this mixed-methods survey study of PICU physician and nurse leaders, tracking and internal reporting of conflicts and outcomes were associated with more objectively applied interventions. The wide-ranging approaches and thresholds for escalation voiced by our respondents indicate a need to develop standardized and evidence-based processes to ensure greater effectiveness by clinical teams and leaders in addressing conflict and reduce potential disparities in outcomes. Respondents shared ideas for preventive and responsive processes that could be implemented and tested in the future. Learning from existing management approaches may help develop standardized, generalizable interventions to reduce conflict, improve interventions, and reduce subjectivity in the application of interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
- doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.9789
Similar articles
-
Evidence Brief: Comparative Effectiveness of Appointment Recall Reminder Procedures for Follow-up Appointments [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2015 Jul. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2015 Jul. PMID: 27606388 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
PICU Provider Supply and Demand: A National Survey.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2018 Aug;19(8):e378-e386. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001587. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29923939
-
Conflict management styles of nurse managers working in inpatient institutions: the case of Turkey.J Nurs Manag. 2018 Nov;26(8):945-952. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12609. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Nurs Manag. 2018. PMID: 30238532
-
Development and evaluation of a de-escalation training intervention in adult acute and forensic units: the EDITION systematic review and feasibility trial.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jan;28(3):1-120. doi: 10.3310/FGGW6874. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38343036 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships Among Nurse Manager Leadership Skills, Conflict Management, and Unit Teamwork.J Nurs Adm. 2018 Jul/Aug;48(7-8):383-388. doi: 10.1097/NNA.0000000000000633. J Nurs Adm. 2018. PMID: 30028814
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous