Perceived effectiveness of endometriosis therapies on fatigue: an international survey
- PMID: 40372805
- PMCID: PMC12084798
- DOI: 10.1530/RAF-25-0010
Perceived effectiveness of endometriosis therapies on fatigue: an international survey
Abstract
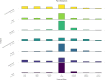
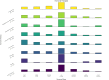
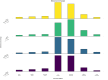
Abstract: Current endometriosis treatments primarily focus on pain management, despite many patients also experiencing fatigue, which significantly impacts their quality of life. This study aimed to evaluate the perceived effectiveness of endometriosis treatments in managing fatigue. An international anonymous survey was conducted using the Qualtrics platform, with participants (aged 16 years and over) and a self-reported diagnosis of endometriosis. The survey collected demographic information, the brief fatigue inventory, and perceived impact of treatments on fatigue over the past 5 years. Ethical approval was granted by the Edinburgh Medical School Research Ethics Committee. Data analysis was performed using R, with results presented as medians and interquartile ranges. From 12 April to 25 May 2023, 2,907 responses were collected. Our results showed that fatigue was significantly worsened during menstruation (median: -2, IQR: -3 to -1) and slightly worsened during ovulation (median: -1, IQR: -2 to 0). Analysis revealed limited associations between common medical treatments, such as analgesics or hormonal therapy, and improvements in fatigue symptoms. Use of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists was linked to a worsened fatigue, reported by 54% users. Surgical interventions and changes in rest patterns showed minimal improvement, while other behavioural modifications showed little to no effect. These findings suggest that current endometriosis treatments are largely ineffective in addressing fatigue. Limitations of this study include recall bias and confounding factors, which may influence perceived effectiveness of endometriosis therapies on fatigue. This underscores the need for more comprehensive management strategies to better support patients experiencing endometriosis-associated fatigue.
Lay summary: Endometriosis is a common chronic pain condition affecting 180 million women worldwide. Many women with endometriosis also report that fatigue significantly impacts their quality of life. Despite this, fatigue management has been largely neglected, and there are limited studies that have evaluated the benefit of current endometriosis treatments on fatigue. This international survey aimed to evaluate the perceived effectiveness of various therapies for endometriosis on fatigue, including pain medication, hormonal medication, surgery and behavioural changes. Pain medication and most hormonal therapies provided limited relief. However, gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists worsened fatigue in more than half of the users. These results suggest that existing endometriosis treatments are largely ineffective in addressing fatigue, highlighting the need for improved strategies to address this symptom to enhance quality of life for women with endometriosis.
Keywords: comprehensive management strategies; endometriosis therapy; fatigue; international survey; medical treatments; surgical interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
LHRW has received grant funding from the NIHR and Roche Diagnostics and honorarium (paid to institution) from Gedeon Richter. AH has received payment for a presentation from Theramex. AH is co-editor in chief of
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preventing recurrence of endometriosis-related pain by means of long-acting progestogen therapy: the PRE-EMPT RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Sep;28(55):1-77. doi: 10.3310/SQWY6998. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39259620 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
A Digital Program for Daily Life Management With Endometriosis: Pilot Cohort Study on Symptoms and Quality of Life Among Participants.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Feb 28;9:e58262. doi: 10.2196/58262. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 39791286 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy in improving quality of life in patients undergoing endometriosis surgery: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 8;11(12):e054896. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-054896. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34880026 Free PMC article.
-
Medical and surgical therapies for pain associated with endometriosis.J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2001 Mar;10(2):137-62. doi: 10.1089/152460901300039485. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2001. PMID: 11268298 Review.
References
-
- Chaichian S, Kabir A, Mehdizadehkashi A, et al. . 2017. Comparing the efficacy of surgery and medical therapy for pain management in endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician 20 185–195. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

