Paper-Based Vertical Flow Assays for in Vitro Diagnostics and Environmental Monitoring
- PMID: 40372939
- PMCID: PMC12117607
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.5c00668
Paper-Based Vertical Flow Assays for in Vitro Diagnostics and Environmental Monitoring
Abstract
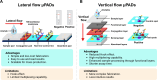
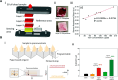
Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) are powerful tools for diagnostic and environmental monitoring. Being affordable and portable, μPADs enable rapid detection of small molecules, heavy metals, and biomolecules, thereby decentralizing diagnostics and expanding biosensor accessibility. However, the reliance on two-dimensional fluid flow restricts the utility of conventional μPADs, presenting challenges for applications that require simultaneous multibiomarker analysis from a single sample. Vertical flow paper-based analytical devices (VF-μPADs) overcome this challenge by allowing axial fluid movement through paper stacks, offering several advantages, including (1) enhanced multiplexing capabilities, (2) reduced hook effect for improved accuracy, and (3) shorter assay times. This review provides an overview of VF-μPADs technologies, exploring structural and functional performance trade-offs between VF-μPADs and conventional lateral flow systems. The sensing performance, fabrication methods, and applications in in vitro diagnostics and environmental monitoring are discussed. Furthermore, critical challenges─such as fabrication complexity, data analysis, and scalability─are addressed, along with proposed strategies for mitigating these barriers to facilitate broader adoption. By examining these strengths and challenges, this review presents the potential of VF-μPADs to advance point-of-care testing, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Environmental monitoring; In vitro diagnostics; Multiplexing; Paper-based analytical devices; Point of care testing; Vertical flow assay; Vertical flow paper-based analytical devices.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

