Investigating the Key Trends in Applying Artificial Intelligence to Health Technologies: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 40372995
- PMCID: PMC12080793
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322197
Investigating the Key Trends in Applying Artificial Intelligence to Health Technologies: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is exponentially rising in the healthcare sector. This change influences various domains of early identification, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases.
Purpose: This study examines the integration of AI in healthcare, focusing on its transformative potential in diagnostics and treatment, and the challenges and methodologies. shaping its future development.
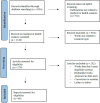
Methods: The review included 68 academic studies retracted from different databases (WOS, Scopus and Pubmed) from January 2020 and April 2024. After careful review and data analysis, AI methodologies, benefits and challenges, were summarized.
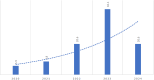
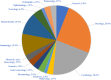
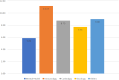
Results: The number of studies showed a steady rise from 2020 to 2023. Most of them were the results of a collaborative work with international universities (92.1%). The majority (66.7%) were published in top-tier (Q1) journals and 40% were cited 2-10 times. The results have shown that AI tools such as deep learning methods and machine learning continue to significantly improve accuracy and timely execution of medical processes. Benefits were discussed from both the organizational and the patient perspective in the categories of diagnosis, treatment, consultation and health monitoring of diseases. However, some challenges may exist, despite these benefits, and are related to data integration, errors related to data processing and decision making, and patient safety.
Conclusion: The article examines the present status of AI in medical applications and explores its potential future applications. The findings of this review are useful for healthcare professionals to acquire deeper knowledge on the use of medical AI from design to implementation stage. However, a thorough assessment is essential to gather more insights into whether AI benefits outweigh its risks. Additionally, ethical and privacy issues need careful consideration.
Copyright: © 2025 Samah, Samar. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence for breast cancer detection and its health technology assessment: A scoping review.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Jan;184:109391. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109391. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39579663
-
The integration of artificial intelligence into clinical medicine: Trends, challenges, and future directions.Dis Mon. 2025 Jun;71(6):101882. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2025.101882. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Dis Mon. 2025. PMID: 40140300
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05989-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40251567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Big Data Analytics, AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning in the Health Care System of Bangladesh: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 28;26:e54710. doi: 10.2196/54710. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39466315 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Healthcare in Low-Resource Settings With Artificial Intelligence: Recent Developments and Outcomes.Public Health Nurs. 2025 Mar-Apr;42(2):1017-1030. doi: 10.1111/phn.13500. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39629887 Review.
References
-
- Ayub Khan A, Ali Laghari A, Rashid M, Li H, Rehman Javed A, Reddy Gadekallu T. Artificial intelligence and blockchain technology for secure smart grid and power distribution Automation: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. 2023;57:103282. doi: 10.1016/j.seta.2023.103282 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

