Polymorphisms in rs2069845 are associated with IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor levels during total joint replacement
- PMID: 40373041
- PMCID: PMC12080868
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312985
Polymorphisms in rs2069845 are associated with IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor levels during total joint replacement
Abstract
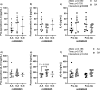
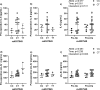
As the number of patients undergoing total joint replacement (TJR) surgery increases, so does the number of revision surgeries. One driver of implant failure and subsequent revision surgery is peri-implant osteolysis, which is driven by inflammation-mediated bone loss. IL-6 is an inflammatory cytokine that is elevated during the peri-operative period. Early elevations in IL-6 levels have been linked to osteolysis development. The current study asked whether there is genetic contribution to the IL-6-related peri-operative inflammatory reaction to TJR surgery. Patients undergoing primary TJR (total hip or total knee) provided pre-operative and post-operative blood samples for measurement of the circulating levels of IL-6 and the soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6r), as well as evaluation of allele status of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) linked to IL-6 or sIL-6r levels - rs2069845, rs2228145, and rs4537545. Circulating sIL-6r levels were associated with allele status in the rs2228145 SNP. More interestingly, allele status in the rs2069845 SNP was associated with the change in circulating IL-6 levels following TJR surgery. Specifically, patients with the A,A allele had increasing levels of IL-6, while those harboring the G,A allele had decreasing levels of IL-6. While implant survival was not assessed, the critical role of IL-6 in peri-implant osteolysis suggests that the rs2069845 allele may influence orthopedic implant success. rs2069845 polymorphisms may be a useful patient-specific marker of inflammatory response to TJR surgery.
Copyright: © 2025 Anderson et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A common variant of the interleukin 6 receptor (IL-6r) gene increases IL-6r and IL-6 levels, without other inflammatory effects.Genes Immun. 2007 Oct;8(7):552-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364414. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Genes Immun. 2007. PMID: 17671508 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble IL-6R-mediated IL-6 trans-signaling activation contributes to the pathological development of psoriasis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Jul;99(7):1009-1020. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02073-3. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33835216
-
Variation in cytokine genes can contribute to severity of acetabular osteolysis and risk for revision in patients with ABG 1 total hip arthroplasty: a genetic association study.BMC Med Genet. 2009 Oct 27;10:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-109. BMC Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19860911 Free PMC article.
-
A pilot study of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 receptor and their effects on pre- and post-transplant serum mediator level and outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Jul;193(1):130-141. doi: 10.1111/cei.13124. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29513361 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genetic susceptibility towards periprosthetic osteolysis.Genes Genomics. 2019 Oct;41(10):1113-1125. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00845-3. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31313107 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

