Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid induces JAK-dependent intracellular activation of human sensory neurons
- PMID: 40373045
- PMCID: PMC12220938
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.186646
Rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid induces JAK-dependent intracellular activation of human sensory neurons
Abstract
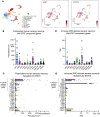
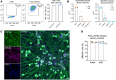
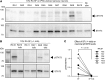
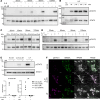
JAK inhibitors (JAKi) are widely used antiinflammatory drugs. Recent data suggest that JAKi have superior effects on pain reduction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the underlying mechanisms for this observation are not fully understood. We investigated whether JAKi can act directly on human sensory neurons. We analyzed RNA-seq datasets of sensory neurons and found that they expressed JAK1 and STAT3. Addition of cell-free RA synovial fluid to human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived (iPSC-derived) sensory neurons led to phosphorylation of STAT3 (pSTAT3), which was completely blocked by the JAKi tofacitinib. Compared with paired serum, RA synovial fluid was enriched for the STAT3 signalling cytokines IL-6, IL-11, LIF, IFN-α, and IFN-β, with their requisite receptors present in peripheral nerves postmortem. Accordingly, these recombinant cytokines induced pSTAT3 in iPSC-derived sensory neurons. Furthermore, IL-6 + sIL-6R and LIF upregulated expression of pain-relevant genes with STAT3-binding sites, an effect that was blocked by tofacitinib. LIF also induced neuronal sensitization, highlighting this molecule as a putative pain mediator. Finally, over time, tofacitinib reduced the firing rate of sensory neurons stimulated with RA synovial fluid. Together, these data indicate that JAKi can act directly on human sensory neurons, providing a potential mechanistic explanation for their suggested superior analgesic properties.
Keywords: Immunology; Inflammation; Neuroscience; Pain; Rheumatology; iPS cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
JAK inhibitors inhibit angiogenesis by reducing VEGF production from rheumatoid arthritis-derived fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Nov;43(11):3525-3536. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07142-9. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39302595
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis naive to methotrexate: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 8;5(5):CD012657. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012657. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28481462 Free PMC article.
-
Role of JAK-STAT signaling in the pathogenic behavior of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: Effect of the novel JAK inhibitor peficitinib.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 5;882:173238. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173238. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32561292
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for rheumatoid arthritis in incomplete responders to methotrexate or other traditional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 13;2016(5):CD012183. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012183. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27175934 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ectopic Nociceptor Sprouting as a Key Peripheral Driver of Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2025 Jul 16;27(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s11926-025-01198-5. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

