LIPID DROPLET PROTEIN OF SEEDS is involved in the control of lipid droplet size in Arabidopsis seeds and seedlings
- PMID: 40373051
- PMCID: PMC12123417
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koaf121
LIPID DROPLET PROTEIN OF SEEDS is involved in the control of lipid droplet size in Arabidopsis seeds and seedlings
Abstract
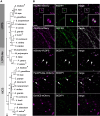
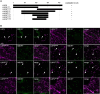
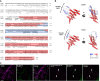
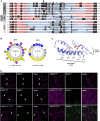
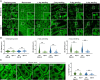
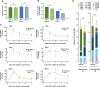
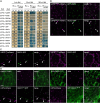
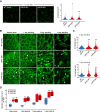
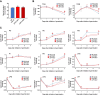
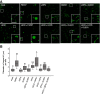
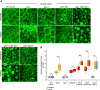
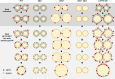
In oilseeds, energy-rich carbon is stored as triacylglycerols in organelles called lipid droplets (LDs). While several of the major biogenetic proteins involved in LD formation have been identified, the full repertoire of LD proteins and their functional roles remains incomplete. Here, we show that the low-abundance, seed-specific LD protein LIPID DROPLET PROTEIN OF SEEDS (LDPS) contains an amphipathic α-helix and proline hairpin motif that serves as an LD-targeting signal and a separate region that binds to the LD protein OLEOSIN 1 (OLEO1). Loss of LDPS function results in smaller LDs and less seed oil in comparison with wild type, while overexpression of LDPS results in an increase in LD size and seed oil content. Loss of LDPS function also results in an inability of LDs to undergo fusion during postgerminative seedling growth. Analysis of oleo1 and ldps single- and double-mutant seeds and freeze-thaw treatment of seeds revealed that OLEO1 suppresses the ability of LDPS to promote larger LDs. Collectively, our results identify LDPS as an important player in LD biology that functions together with OLEO1 to determine LD size in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) seeds and seedlings through a process that involves LD-LD fusion.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Barneda D, Planas-Iglesias J, Gaspar ML, Mohammadyani D, Prasannan S, Dormann D, Han G-S, Jesch SA, Carman GM, Kagan V, et al. The brown adipocyte protein CIDEA promotes lipid droplet fusion via a phosphatidic acid-binding amphipathic helix. eLife. 2015:4:e07485. 10.7554/eLife.07485 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RGPIN-2018-04629/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- RGPIN-2022-03459/Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- DE-SC0016536/US Department of Energy, Office of Science, BES-Physical Biosciences program
- 2020-21000-013-00D/US Department of Agriculture-Agriculture Research Service
- IS 273/2-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

