SOX7: Autism associated gene identified by analysis of multi-Omics data
- PMID: 40373085
- PMCID: PMC12080844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320096
SOX7: Autism associated gene identified by analysis of multi-Omics data
Abstract
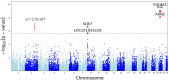
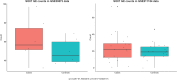
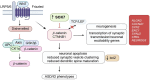
Genome-wide association studies and next generation sequencing data analyses based on DNA information have identified thousands of mutations associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). However, more than 99% of identified mutations are non-coding. Thus, it is unclear which of these mutations might be functional and thus potentially causal variants. Transcriptomic profiling using total RNA-sequencing has been one of the most utilized approaches to link protein levels to genetic information at the molecular level. The transcriptome captures molecular genomic complexity that the DNA sequence solely does not. Some mutations alter a gene's DNA sequence but do not necessarily change expression and/or protein function. To date, few common variants reliably associated with the diagnosis status of ASD despite consistently high estimates of heritability. In addition, reliable biomarkers used to diagnose ASD or molecular mechanisms to define the severity of ASD do not exist. Therefore, it is necessary to integrate DNA and RNA testing together to identify true causal genes and propose useful biomarkers for ASD. We performed gene-based association studies with adaptive test using genome-wide association studies' (GWAS) summary statistics with two large GWAS datasets (ASD 2019 data: 18,382 ASD cases and 27,969 controls [discovery data]; ASD 2017 data: 6,197 ASD cases and 7,377 controls [replication data]) which were obtained from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC). In addition, we investigated differential expression between ASD cases and controls for genes identified in gene-based GWAS with two RNA-seq datasets (GSE211154: 20 cases and 19 controls; GSE30573: 3 cases and 3 controls). We identified 5 genes significantly associated with ASD in ASD 2019 data (KIZ-AS1, p = 8.67 × 10-10; KIZ, p = 1.16 × 10-9; XRN2, p = 7.73 × 10-9; SOX7, p = 2.22 × 10-7; LOC101929229 also known as PINX1-DT, p = 2.14 × 10-6). Among these 5 genes, gene SOX7 (p = 0.00087) and LOC101929229 (p = 0.009) were replicated in ASD 2017 data. KIZ-AS1 (p = 0.059) and KIZ (p = 0.06) were close to the boundary of replication in ASD 2017 data. Genes SOX7 (p = 0.036 in all samples; p = 0.044 in white samples) indicated significant expression differences between cases and controls in the GSE211154 RNA-seq data. Furthermore, gene SOX7 was upregulated in cases than in controls in the GSE30573 RNA-seq data (p = 0.0017; Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted p = 0.0085). SOX7 encodes a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors pivotally contributing to determining of the cell fate and identity in many lineages. The encoded protein may act as a transcriptional regulator after forming a protein complex with other proteins leading to autism. Gene SOX7 in the transcription factor family could be associated with ASD. This finding may provide new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for ASD.
Copyright: © 2025 Gonzales et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Update of
-
SOX7: Autism Associated Gene Identified by Analysis of Multi-Omics Data.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 9:2023.05.26.542456. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.26.542456. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0320096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320096. PMID: 37292933 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SOX7: Novel Autistic Gene Identified by Analysis of Multi-Omics Data.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 14:rs.3.rs-3346245. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3346245/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0320096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320096. PMID: 37790478 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
SOX7: Autism Associated Gene Identified by Analysis of Multi-Omics Data.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 9:2023.05.26.542456. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.26.542456. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0320096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320096. PMID: 37292933 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SOX7: Novel Autistic Gene Identified by Analysis of Multi-Omics Data.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 14:rs.3.rs-3346245. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3346245/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 May 15;20(5):e0320096. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320096. PMID: 37790478 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Novel Insight Into the Etiology of Autism Spectrum Disorder Gained by Integrating Expression Data With Genome-wide Association Statistics.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 15;86(4):265-273. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.04.034. Epub 2019 May 11. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31230729 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture of autism spectrum disorder: Lessons from large-scale genomic studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Sep;128:244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.028. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34166716 Review.
-
SOX7: from a developmental regulator to an emerging tumor suppressor.Histol Histopathol. 2014 Apr;29(4):439-45. doi: 10.14670/HH-29.10.439. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Histol Histopathol. 2014. PMID: 24288056 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

