Multi-assistant methods improve stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) assessment in breast cancer: results of multi-institutional ring studies
- PMID: 40373351
- PMCID: PMC12141058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105095
Multi-assistant methods improve stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) assessment in breast cancer: results of multi-institutional ring studies
Abstract
Background: Stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (sTILs) have significant prognostic value for breast cancer patients, but its accurate assessment can be very challenging. We comprehensively studied the pitfalls faced by pathologists with different levels of professional experience, and explored clinical applicability of reference cards (RCs)- and artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted methods in assessing sTILs.
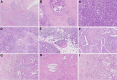
Materials and methods: Three rounds of ring studies (RSs) involving 12 pathologists from four hospitals were conducted. AI algorithms based on the field of view (FOV) and whole section were proposed to create RCs and to compute whole-slide image interpretations, respectively. Stromal regions identified and the associated sTIL scores by the AI method were provided to the pathologists as references. Fifty cases of surgical resections were used for interobserver concordance analysis in RS1. A total of 200 FOVs with challenge factors were assessed in RS2 for accuracy of the RC-assisted and AI-assisted methods, while 167 cases were used to validate their clinical performance in RS3.
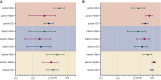
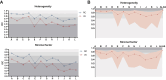
Results: With the assistance of RCs, the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) in RS1 increased significantly to 0.834 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.772-0.889]. The largest enhancement in ICC, from moderate (ICC: 0.592; 95% CI 0.499-0.677) to good (ICC: 0.808; 95% CI 0.746-0.857) was observed for heterogeneity. Accuracy evaluation showed significant grade improvement for heterogeneity and stromal factor FOVs among senior, intermediate, and junior groups. The ICC of heterogeneity and stromal factor analysis by the AI-assisted method achieved a level comparable to that of the senior group with RC assistance. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, denoted as AUC, for AI-assisted sTIL scores in predicting pathological complete response after neoadjuvant therapy was 0.937, which was superior to visual assessment with an AUC of 0.775.
Conclusion: RC- and AI-assisted technology can reduce the uncertainty of interpretation caused by heterogeneous distribution.
Keywords: AI; breast cancer; concordance; reference card; stromal TILs.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reproducibility and predictive value of scoring stromal tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: a multi-institutional study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Aug;171(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4825-8. Epub 2018 May 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29774470
-
Improving Ki67 assessment concordance by the use of an artificial intelligence-empowered microscope: a multi-institutional ring study.Histopathology. 2021 Oct;79(4):544-555. doi: 10.1111/his.14383. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Histopathology. 2021. PMID: 33840132
-
The importance of stromal and intratumoral tumor lymphocyte infiltration for pathologic complete response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Apr-Jun;14(3):619-624. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.174550. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29893329
-
Training pathologists to assess stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer synergises efforts in clinical care and scientific research.Histopathology. 2024 May;84(6):915-923. doi: 10.1111/his.15140. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Histopathology. 2024. PMID: 38433289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating multi-omics data with artificial intelligence to decipher the role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in tumor immunotherapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Jul;271:156035. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.156035. Epub 2025 May 23. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40435910 Review.
References
-
- Denkert C., von Minckwitz G., Darb-Esfahani S., et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(1):40–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

