Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome for inflammatory disease therapy
- PMID: 40374417
- PMCID: PMC12570976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2025.04.007
Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome for inflammatory disease therapy
Abstract
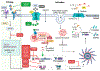
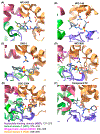
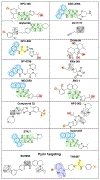
The NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a megadalton complex implicated in numerous inflammation-driven diseases including COVID-19, Alzheimer's disease, and gout. Although past efforts have focused on inhibiting IL-1β downstream of NLRP3 activation using drugs such as canakinumab, no FDA-approved NLRP3-targeted inhibitors are currently available. MCC950, a direct NLRP3 inhibitor, showed promise but exhibited off-target effects. Recent research has focused on optimizing the sulfonylurea-based MCC950 scaffold by leveraging recent structural and medicinal chemistry insights into the NLRP3 nucleotide-binding and oligomerization (NACHT) domain to improve solubility and clinical efficacy. In addition, oxidized DNA (oxDNA) has emerged as a key inflammasome trigger, and molecules targeting the pyrin domain have shown promise in inhibiting NLRP3 activation. This review discusses the role of NLRP3 in inflammation-related diseases, the status of ongoing clinical trials, and emerging small-molecule therapeutics targeting NLRP3.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; ROS; SU0268; TH5487; mtDNA.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The University of California Irvine is in the process of filling a patent with J.C., A.L., and R.M. listed as inventors.
Figures
References
-
- Mosley B et al. (1987) The interleukin-1 receptor binds the human interleukin-1 alpha precursor but not the interleukin-1 beta precursor. J. Biol. Chem 262, 2941–2944 - PubMed
-
- Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M (2024) Drugging the NLRP3 inflammasome: from signalling mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 23, 43–66 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

