Pinosylvin and Sanguinarine Combination to Enhance Antifungal Activity against Candida albicans
- PMID: 40374536
- PMCID: PMC12099613
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2412.12055
Pinosylvin and Sanguinarine Combination to Enhance Antifungal Activity against Candida albicans
Abstract
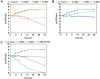
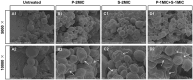
Candida albicans is one of the major sources of fungal infections that can lead to life-threatening systemic infections. However, effective control of C. albicans remains a great challenge. Herein, this study aimed at investigating the antifungal effect of a combination of two natural compounds, pinosylvin (PIN) and sanguinarine (SAN), against C. albicans. In order to investigate the antifungal effect and mechanism of the combination of PIN and SAN, antimicrobial assay, time-kill assay, biofilm formation assay, cell membrane integrity assay, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) assay were performed. The results showed that the combination of PIN and SAN was more effective against C. albicans than PIN or SAN alone. PIN and SAN could jointly inhibit biofilm formation and thus attenuate C. albicans adhesion and colonization ability. PIN mainly targeting the cell membrane while SAN mainly inducing the cell to produce large amounts of ROS. Besides, PIN promoted the entry of SAN into C. albicans. Finally, the hemolysis experiment demonstrated that the combination of PIN and SAN is biocompatible. Taken together, the combination of PIN and SAN enhanced the antifungal effect against C. albicans, which has a broad application prospect in the control of C. albicans.
Keywords: Candida albicans; antifungal; pinosylvin; sanguinarine; synergy effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

