Multi-institutional atlas of brain metastases informs spatial modeling for precision imaging and personalized therapy
- PMID: 40374598
- PMCID: PMC12081687
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59584-7
Multi-institutional atlas of brain metastases informs spatial modeling for precision imaging and personalized therapy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Multi-institutional atlas of brain metastases informs spatial modeling for precision imaging and personalized therapy.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 2;16(1):5096. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60522-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40456774 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
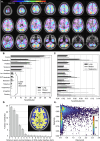
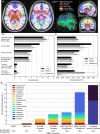
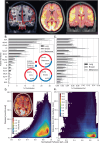
Brain metastases are a frequent and debilitating manifestation of advanced cancer. Here, we collect and analyze neuroimaging of 3,065 cancer patients with 13,067 brain metastases, representing an extensive collection for research. We find that metastases predominantly localize to high perfusion areas near the grey-white matter junction, but also identify notable differences depending on the primary cancer histology as well as brain regions which do not conform to this relationship. Lung and breast cancers, in contrast to melanoma, frequently metastasize to the cerebellum, hinting at biological pathways of spread. Additionally, the deep brain structures are relatively spared from metastasis, regardless of primary cancer type. Leveraging this data, we propose a probabilistic brain metastasis risk model to enhance the therapeutic ratio of whole-brain radiotherapy by targeting high risk areas while preserving cortical and subcortical brain regions of functional significance and low metastasis risk, potentially reducing the cognitive side effects of therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

