Tandem ketone reduction in pepstatin biosynthesis reveals an F420H2-dependent statine pathway
- PMID: 40374670
- PMCID: PMC12081711
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59785-0
Tandem ketone reduction in pepstatin biosynthesis reveals an F420H2-dependent statine pathway
Abstract
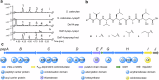
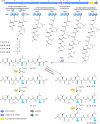
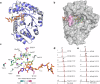
Pepstatins are potent inhibitors of aspartic proteases, featuring two statine residues crucial for target binding. However, the biosynthesis of pepstatins, especially their statine substructure, remains elusive. Here, we discover and characterize an unconventional gene cluster responsible for pepstatin biosynthesis, comprising discrete nonribosomal peptide synthetase and polyketide synthase genes, highlighting its trans-acting and iterative nature. Central to this pathway is PepI, an F420H2-dependent oxidoreductase. The biochemical characterization of PepI reveals its role in the tandem reduction of β-keto pepstatin intermediates. PepI first catalyzes the formation of the central statine, then produces the C-terminal statine moiety. The post-assembly-line formation of statine by PepI contrasts with the previously hypothesized biosynthesis involving polyketide synthase ketoreductase domains. Structural studies, site-directed mutagenesis, and deuterium-labeled enzyme assays probe the mechanism of F420H2-dependent oxidoreductases and identify critical residues. Our findings uncover a unique statine biosynthetic pathway employing the only known iterative F420H2-dependent oxidoreductase to date.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
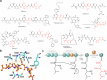

Similar articles
-
Characterization of Miharamycin Biosynthesis Reveals a Hybrid NRPS-PKS to Synthesize High-Carbon Sugar from a Complex Nucleoside.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Apr 1;142(13):5996-6000. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c01778. Epub 2020 Mar 17. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32167762
-
Directed Accumulation of Anticancer Depsipeptides by Characterization of Neoantimycins Biosynthetic Pathway and an NADPH-Dependent Reductase.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Aug 17;13(8):2153-2160. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00325. Epub 2018 Jul 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29979567
-
Chain initiation in the leinamycin-producing hybrid nonribosomal peptide/polyketide synthetase from Streptomyces atroolivaceus S-140. Discrete, monofunctional adenylation enzyme and peptidyl carrier protein that directly load D-alanine.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jul 13;282(28):20273-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702814200. Epub 2007 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17502372
-
Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Modular Polyketide Synthase Ketoreductase Domains for Altered Stereochemical Control.Chembiochem. 2021 Apr 6;22(7):1122-1150. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000613. Epub 2020 Dec 22. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33185924 Review.
-
[The PKS/NRPS hetero-gene cluster of epothilones].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003 Sep;19(5):511-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 15969075 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Kunimoto, S., Aoyagi, T., Morishima, H., Takeuchi, T. & Umezawa, H. Mechanism of inhibition of pepsin by pepstatin. J. Antibiot.25, 251–255 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi, T., Morishima, H., Nishizawa, R., Kunimoto, S. & Takeuchi, T. Biological activity of pepstatins, pepstanone A and partial peptides on pepsin, cathepsin D and renin. J. Antibiot.25, 689–694 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Marks, N., Grynbaum, A. & Lajtha, A. Pentapeptide (pepstatin) inhibition of brain acid proteinase. Science181, 949–951 (1973). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

