Autologous HIV-specific T cell therapy targeting conserved epitopes is well-tolerated in six adults with HIV: an open-label, single-arm phase 1 study
- PMID: 40374689
- PMCID: PMC12081906
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59810-2
Autologous HIV-specific T cell therapy targeting conserved epitopes is well-tolerated in six adults with HIV: an open-label, single-arm phase 1 study
Abstract
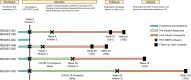
Novel cellular therapies may enable HIV control or cure. HIV-specific T cells targeting conserved immunogenic protein regions of HIV Gag/Pol and the entirety of HIV Nef, termed HST-NEETs, eliminate HIV infected cells in vitro. Here we enroll seven participants in an open-label, single-arm phase 1 study (NCT03485963) to evaluate the safety (primary endpoint) of two autologous administrations of HST-NEET products without prescribed lymphodepletion. Adults with well-controlled HIV on anti-retroviral therapy are eligible. Six participants completed safety monitoring. No serious product-related toxicities are observed. Secondary endpoints are to assess expansion and persistence of HIV-reactive T cell clones, and changes to the HIV reservoir for each infused participant. HIV-specific T cell and HIV anti-Env antibody responses increase in two participants after infusion two. A trend towards decreasing levels of intact proviruses is observed in 2 participants. Three participants show persistence of HIV-reactive, product-associated T cell clones for ≥40 weeks post infusions. HST-NEETs infusions are well-tolerated. Future trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy of HST-NEETs in this population.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: C.M.B. is on the Board of Directors of Cabaletta Bio and was the scientific co-founder and scientific advisory board member of Catamaran Bio, has stock in Repertoire Immune Medicines and serves on the data and safety monitoring board (DSMB) of the Swedish Orphan Biovitrum (SOBI). PJH is an advisor or member of on an advisory board of Autolomous, CARTx, Celleknos, Cipla, March Biosciences, MFX, and Y Innovations. M.D.K. is an author for Elsevier (Uptodate) and has received research funding from Chiesi Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Finzi, D. et al. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science278, 1295–1300 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Wong, J. K. et al. Recovery of replication-competent HIV despite prolonged suppression of plasma viremia. Science278, 1291–1295 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Finzi, D. et al. Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat. Med.5, 512–517 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

