Relationship between adolescent gaming addiction and myopia, ocular surface condition, and health status: a questionnaire based cohort study
- PMID: 40374701
- PMCID: PMC12081934
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-96671-7
Relationship between adolescent gaming addiction and myopia, ocular surface condition, and health status: a questionnaire based cohort study
Abstract
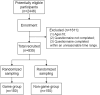
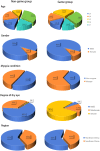
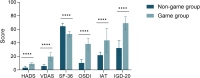
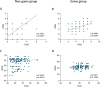
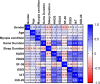
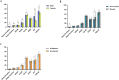
This study explores the relationship between gaming addiction among Chinese adolescents and their myopia, ocular surface conditions, and overall health. A cross-sectional questionnaire-based cohort study included 835 participants aged 13-17, selected from 3300. Tools included the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Van Dream Anxiety Scale (VDAS), 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36), Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), Internet Addiction Test (IAT), and Internet Gaming Disorder Scale-20 (IGD-20). Linear regression, Pearson correlation, and unpaired t-tests were used. Gaming addiction correlated with worsened physical and mental health. Older age and longer gaming duration were linked to higher myopia rates. Males scored higher on HADS, VDAS, IAT, and IGD-20 but lower on SF-36 than females. Myopic gamers had longer gaming durations and higher IAT scores. IGD-20 scores for gamers playing 5-6+ hours daily showed stronger correlations with HADS, VDAS, and OSDI. Online gaming significantly impacts vision, physical and mental health, and ocular surface conditions. Score differences between groups underscore the need for interventions, including mental health support, cognitive-behavioral correction, and preventive eye care.
Keywords: Adolescents; Internet game addiction; Myopia; Ocular surface; Physical health; Psychological health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study methods and protocols were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University (Nanchang, China) and followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The guardians of the adolescent participants have given informed consent for their participating in the questionnaire survey.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cognitive Mechanisms Between Psychosocial Resources and the Behavioral Intention of Professional Help-Seeking for Internet Gaming Disorder Among Chinese Adolescent Gamers: Cross-Sectional Mediation Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Nov 14;10:e52478. doi: 10.2196/52478. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39588703 Free PMC article.
-
Internet gaming disorder in male and female young adults: The role of alexithymia, depression, anxiety and gaming type.Psychiatry Res. 2019 Feb;272:521-530. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.12.158. Epub 2018 Dec 29. Psychiatry Res. 2019. PMID: 30616119
-
Impact of internet gaming disorder on mental well-being: prevalence and psychological distress among adolescents and young adults.Psychiatry Res. 2025 Jul;349:116512. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2025.116512. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Psychiatry Res. 2025. PMID: 40318564
-
Awareness and Potential Impacts of the Medicalization of Internet Gaming Disorder: Cross-sectional Survey Among Adolescents in China.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Feb 24;23(2):e22393. doi: 10.2196/22393. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33625362 Free PMC article.
-
Internet Gaming Disorder: An Emergent Health Issue for Men.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):1151-1159. doi: 10.1177/1557988318766950. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29606034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stevens, M. W., Dorstyn, D., Delfabbro, P. H. & King, D. L. Global prevalence of gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry55, 553–568. 10.1177/0004867420962851 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Sussman, C. J., Harper, J. M., Stahl, J. L. & Weigle, P. Internet and video game addictions: Diagnosis, epidemiology, and neurobiology. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N Am.27, 307–326. 10.1016/j.chc.2017.11.015 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

