Far-Infrared Radiation Ameliorates the Cognitive Dysfunction in an Alzheimer's Disease Transgenic Mouse via Modulating Jak-2/Stat3 and Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathways
- PMID: 40374872
- PMCID: PMC12081534
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-025-08860-2
Far-Infrared Radiation Ameliorates the Cognitive Dysfunction in an Alzheimer's Disease Transgenic Mouse via Modulating Jak-2/Stat3 and Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathways
Abstract
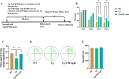
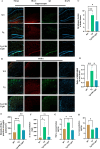
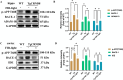
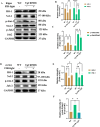
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the primary cause of dementia in the elderly. However, effective therapies that modify the disease process in AD remain elusive. Far-infrared radiation (FIR) is commonly utilized as a complementary treatment a range of disease, for example insomnia and rheumatoid arthritis. In this research, we explored how FIR light impacts the cognitive functions of TgCRND8 AD mice and elucidated its underlying molecular mechanism. The cognitive capabilities of TgCRND8 mice assessed by employing the Morris water maze. The concentrations of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-4, Aβ40, and Aβ42 protein were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Immunostaining was conducted to assess the Aβ deposits and microglial presence in the brains of TgCRND8 mice. Western blot was applied to detect the protein expressions of tau phosphorylation, amyloid-β (Aβ) production, Jak-2/Stat3, and Nrf-2/HO-1 pathways. The results indicated that FIR light notably ameliorated the cognitive impairments of the AD mice, reduced both Aβ deposition and tau protein hyperphosphorylation at sites of Thr205, Ser369, Ser404, and Thr181, suppressed the release of TNF-α and IL-1β, attenuated the ratios of p-Jak-2/Jak-2 and p-Stat3/Stat3, while increased the protein levels of IL-4, Nrf-2, and HO-1 in the brains of TgCRND8 mice. These findings amply demonstrated that FIR light ameliorated cognitive deficits of TgCRND8 mice via reducing both Aβ burden and tau protein hyperphosphorylation, suppressing the neuroinflammation, and restoring the levels of the oxidative-related proteins through modulating Jak-2/Stat3 and Nrf-2/HO-1 pathways. These experimental findings indicate that FIR light treatment is a promising treatment approach for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cognitive dysfunction; Far-infrared radiation; Jak-2/Stat3 pathway; Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway; TgCRND8 mice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for Publication: All authors have consented for publication.
Figures

References
-
- Barthélemy, N. R., Li, Y., Joseph-Mathurin, N., Gordon, B. A., Hassenstab, J., Benzinger, T. L. S., Buckles, V., Fagan, A. M., Perrin, R. J., Goate, A. M., Morris, J. C., Karch, C. M., Xiong, C., Allegri, R., Mendez, P. C., Berman, S. B., Ikeuchi, T., Mori, H., Shimada, H., … McDade, E. (2020). A soluble phosphorylated tau signature links tau, amyloid and the evolution of stages of dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Medicine,26(3), 398–407. 10.1038/s41591-020-0781-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barthélemy, N. R., Mallipeddi, N., Moiseyev, P., Sato, C., & Bateman, R. J. (2019). Tau phosphorylation rates measured by mass spectrometry differ in the intracellular brain vs. extracellular cerebrospinal fluid compartments and are differentially affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.,11, 121. 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00121 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, R. F., Liu, K. F., Lee, S. S., Huang, S. H., Wu, Y. C., Lin, Y. N., Wang, C. T., & Kuo, Y. R. (2021). Far-infrared therapy accelerates diabetic wound healing via recruitment of tissue angiogenesis in a full-thickness wound healing model in rats. Biomedicines,9(12), 1922. 10.3390/biomedicines9121922 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, X., Zhang, H., Zeng, W., Wang, N., Lo, H. H., Ip, C. K., Yang, L. J., Hsiao, W. L. W., Sin, W. M., Xia, C., Law, B. Y. K., & Wong, V. K. W. (2022). Far infrared irradiation suppresses experimental arthritis in rats by down-regulation of genes involved inflammatory response and autoimmunity. Journal of Advanced Research,38, 107–118. 10.1016/j.jare.2021.08.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

