Chondrocyte lysates activate NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis in synovial fibroblasts to exacerbate knee synovitis by downregulating caveolin-1
- PMID: 40375346
- PMCID: PMC12083164
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03573-0
Chondrocyte lysates activate NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis in synovial fibroblasts to exacerbate knee synovitis by downregulating caveolin-1
Abstract
Background: Synovitis, among the most common signs of early-stage osteoarthritis (OA), is mainly mediated by fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). Cartilage destruction creates chondrocyte lysates (CLs) that activate synovial inflammation. A comprehensive understanding of chondrocyte-FLS communication might offer novel, specific therapeutic targets for treating synovitis and OA. Hence, we sought to uncover the specific role of CLs in OA-FLSs and synovitis.
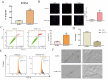
Methods: Isolated CLs were cocultured with FLSs to test whether they could stimulate synovial inflammation. A model of medial meniscus destabilization was prepared in C57BL/6 mice and NLRP3 knockout mice, and adeno-associated virus overexpressing Caveolin-1 (CAV1) was intra-articularly injected for 8 weeks once a week after dissection of the medial meniscus (DMM). Proteins expressed in FLSs with and without CL coculture were screened using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to identify CL-specific regulators of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis.
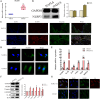
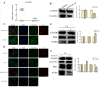
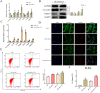
Results: CLs were engulfed by FLSs, which aggravated inflammatory cytokine release and NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated FLS pyroptosis. NLRP3 expression was significantly upregulated in human OA-FLSs and FLSs cocultured with CLs, while CAV1 was downregulated. CAV1 overexpression reversed the inflammatory phenotype in FLSs and simultaneously rescued pyroptosis in CL-pre-treated FLSs. Both synovial hyperplasia and inflammatory infiltration in C57BL/6 mice with DMM surgery were alleviated after intra-articular AAV-CAV1 injection. Moreover, the CL-specific protein LIM-containing lipoma preferred partner (LPP) markedly exacerbated FLS pyroptosis and inflammation.
Conclusions: CLs were endocytosed by FLSs through CAV1, and the CL-specific protein LPP stimulated NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis and synovitis by inhibiting CAV1 expression. Our findings offer a novel therapeutic target for treating synovitis.
Keywords: Caveolin-1; Chondrocyte lysate; Fibroblast-like synoviocyte; LIM-containing lipoma preferred partner; NLRP3.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All experiments involving animal and patient samples in this study adhered to ethical policies and procedures approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, China. (Approval no. IRB: IIT-2021-667; SYSU-IACUC-2020-000504). Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Millerand M, Berenbaum F, Jacques C. Danger signals and inflammaging in osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(Suppl 120):48–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZR2024QH552/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- 82202735/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82172467/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023A1515010142, 2024A1515011189/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China
- 2021B1515020008/Guangdong Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

