The relationship between emotional impulsivity (Urgency), aggression, and symptom dimensions in patients with borderline personality disorder
- PMID: 40375352
- PMCID: PMC12083163
- DOI: 10.1186/s40479-025-00292-5
The relationship between emotional impulsivity (Urgency), aggression, and symptom dimensions in patients with borderline personality disorder
Erratum in
-
Correction: The relationship between emotional impulsivity (Urgency), aggression, and symptom dimensions in patients with borderline personality disorder.Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2025 May 30;12(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40479-025-00298-z. Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2025. PMID: 40448163 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: A hallmark of borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a disposition to anger, irritability and aggression. High impulsivity, particularly high emotional impulsivity (urgency), has been associated with aggression in BPD patients.
Aims: This study aimed to explore, in a sample of patients with BPD, the subtleties of the relationship between borderline symptomatology, different facets of impulsivity, and an aggressive disposition.
Methods: Two hundred and twenty patients with a DSM-5 (Sect. 2) diagnosis of BPD were assessed on measures of impulsivity (UPPS model), aggression (Brief Aggression Questionnaire, BAQ-12) and borderline symptoms (Borderline Personality Questionnaire, BPQ).
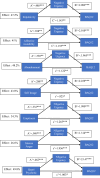
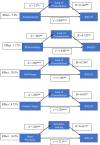
Results: Results showed: (i) there was a close relationship between BPD symptomatology and an aggressive predisposition measured by BAQ-12; (ii) emptiness and intense anger were the BPD symptom dimensions most significantly associated with aggression (iii) both negative and positive urgency, and to a lesser extent lack of premeditation and sensation seeking, mediated the relationship between borderline symptom dimensions and aggression.
Discussion & conclusion: Results suggest a close relationship between almost all dimensions of BPD, but especially anger, and impulsive aggression. They further suggest that urgency, particularly negative urgency, mediates this relationship. Future studies will need to parse aggression into motivationally distinct types.
Keywords: Aggression; Anger; Borderline personality disorder; Impulsivity; Irritability; Negative Urgency; Positive Urgency; UPPS; Urgency.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval is deemed unnecessary according to domestic regulations (Loi Jardé, RIPH3 in 2012, amendment No 2022 − 582 du 20 Avril 2022- art2). The authors followed Helsinki’s and Madrid’s recommendations regarding research involving human participants. All participants signed informed consent to participate in the research and data usage for research and usage of the data for research and teaching purposes. Consent for publication: All participants gave their consent for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Leichsenring F, Leibing E, Kruse J, New AS, Leweke F. Borderline personality disorder. Lancet. 2011;377(9759):74–84. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association D, American Psychiatric Association D. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. Washington, DC: American psychiatric association; 2013.
-
- Organization WH. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems: alphabetical index. World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- Bresin K. Impulsivity and aggression: A meta-analysis using the UPPS model of impulsivity. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;48:124–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

