If a Child Vomits After an Oral Medication-Should We Re-Dose or Not?
- PMID: 40375445
- PMCID: PMC12420867
- DOI: 10.1111/apa.70121
If a Child Vomits After an Oral Medication-Should We Re-Dose or Not?
Abstract
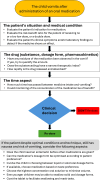
Vomiting after oral administration of medication is common in children. Despite this, there is a lack of formal guidelines and recommendations on this topic. This article is intended for doctors and nurses who treat children to support the management of this everyday clinical dilemma. This article describes the development of a decision support tool and provides an overview of factors to consider. The decision support tool provides advice for making informed decisions. It was based on a literature search combined with an informal consensus discussion in a group of paediatricians, clinical pharmacologists, and clinical pharmacists, followed by an internal review. The decision support tool is now in clinical use.
Keywords: oral medication; paediatric; re‐dosing; vomiting.
© 2025 The Author(s). Acta Paediatrica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Foundation Acta Paediatrica.
Figures
References
-
- Thangaraju P., Natha J. S., Venkatesan S., and Tanguturi Yella S. S., “A Survey From a Tertiary Care Hospital in India on Pediatric Medication Re‐Dosing Practices After Patient Vomiting,” Journal of Pediatric Pharmacology and Therapeutics 27, no. 5 (2022): 457–462, 10.5863/1551-6776-27.5.457. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- The Swedish National Formulary for Children ePed, https://eped.se/about‐eped/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical