Incidence, prevalence, and burden of type 2 diabetes in China: Trend and projection from 1990 to 2050
- PMID: 40375461
- PMCID: PMC12180826
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003536
Incidence, prevalence, and burden of type 2 diabetes in China: Trend and projection from 1990 to 2050
Abstract
Background: The epidemiological pattern and disease burden of type 2 diabetes have been shifting in China over the past decades. This analysis described the epidemiological transition of type 2 diabetes in the past three decades and projected the trend in the future three decades in China.
Methods: Age-, sex-, and year-specific incidence, prevalence, death, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for people with 15 years or older and diabetes or high fasting glucose in China and related countries from 1990 to 2021 were obtained from the Global Burden of Disease. We obtained the trends of age-, sex-, and year-specific rates and absolute numbers of incidence, prevalence, deaths, and DALYs attributable to type 2 diabetes in China from 1990 to 2021. Using the Lee-Carter model, we projected the incidence, prevalence, death, and DALYs attributable to type 2 diabetes to 2050 stratified by age and sex.
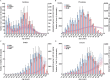
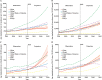
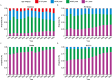
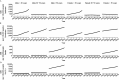
Results: The age-standardized incidence of type 2 diabetes was 341.5 per 100,000 persons (1.6 times in 1990) and the age-standardized prevalence was 9.96% (9960.0 per 100,000 persons, 2.5 times in 1990) in China 2021. In 2021, there were 0.9 million deaths and 26.8 million DALYs due to type 2 diabetes or hyperglycemia, as 2.9 and 2.7 times the data in 1990, respectively. The age-standardized rates of type 2 diabetes and hyperglycemia were projected to raise to 449.5 per 100,000 persons for incidence, 18.17% for prevalence, 244.6 per 100,000 persons for death, and 4720.2 per 100,000 persons for DALYs by 2050. The incidence of type 2 diabetes kept growing among individuals under the age of 20 years in the past three decades (128.7 per 100,000 persons in 1990 and 439.9 per 100,000 persons in 2021) and estimating 1870.8 per 100,000 in 2050.
Conclusions: The incidence, prevalence, and disease burden of type 2 diabetes grew rapidly in China in the past three decades. The prevention of type 2 diabetes in young people and the care for elder adults will be the greatest challenge for the country.
Keywords: Burden; Death; Disability-adjusted life years; Incidence; Prevalence; Projections; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaboration . Cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mortality burden of cardiometabolic risk factors from 1980 to 2010: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2:634–647. doi: 10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70102-0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017;389:2239–2251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)30058-2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

