Effect of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Toceranib on Cardiac Function and Endothelial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Dogs With Cancer
- PMID: 40375566
- PMCID: PMC12081826
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.70115
Effect of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Toceranib on Cardiac Function and Endothelial Dysfunction Biomarkers in Dogs With Cancer
Abstract
Background: Hypertension is documented in dogs with cancer receiving toceranib, but no studies have evaluated left ventricular (LV) systolic function and biomarkers of endothelial function.
Objectives: To characterize changes in echocardiographic variables and biomarkers of endothelial function in dogs treated with toceranib.
Animals: Twenty-six client-owned dogs with no evidence of pre-existing cardiac disease or systemic hypertension are receiving a single agent toceranib for cancer treatment.
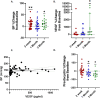
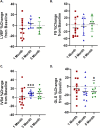
Methods: Dogs were enrolled in this prospective observational study with study visits at baseline, 1, 3, and 5 months after starting toceranib for echocardiographic exams, blood and urine collection, and blood pressure measurements, with an additional blood pressure obtained 2 weeks after starting toceranib. Serum markers of vascular endothelial function (VEGF, endothelin-1, platelet derived growth factor [PDGF], prostacyclin, cyclic guanosine monophosphate [cGMP]) and urinary nitrate were evaluated with ELISA.
Results: Dogs were enrolled between 2019 and 2023. Systolic blood pressure increased 2 weeks after initiating toceranib treatment (p = 0.009). Serum prostacyclin concentration was lower after 1 month of treatment (mean 98.8 pg/mL vs. 140.0 pg/mL at baseline, p = 0.03), and serum VEGF concentration was higher after 3 months of treatment (mean of 247.8 pg/mL vs. 135.4 pg/mL at baseline, p = 0.01). Global longitudinal strain (GLS) decreased at the five-month time point (mean -14.5% vs. -15.7% at baseline, p = 0.048) with no significant change in LV fractional shortening by M-mode or ejection fraction by Simpson's method of discs.
Conclusions: Dogs treated with toceranib might have higher systemic blood pressure associated with changes in VEGF and prostacyclin and decreased systolic function.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; global longitudinal strain; tyrosine kinase inhibitor; vasculotoxicity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Orphanos G. S., Ioannidis G. N., and Ardavanis A. G., “Cardiotoxicity Induced by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors,” Acta Oncologica 48 (2009): 964–970. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R. J., Hutson T. E., Tomczak P., et al., “Sunitinib Versus Interferon Alfa in Metastatic Renal‐Cell Carcinoma,” New England Journal of Medicine 356 (2007): 115–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

