Independent prognostic importance of endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX) in critically ill patients with heart failure: modulating role of inflammation
- PMID: 40375932
- PMCID: PMC12078299
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1560947
Independent prognostic importance of endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX) in critically ill patients with heart failure: modulating role of inflammation
Abstract
Background: The connection between endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX) and risk of mortality in critically ill patients with heart failure (HF) remains unclear. This research sought to explore this relationship.
Methods: MIMIC-IV database (version 3.1) was utilized to provide clinical data. Due to the non-normal distribution, EASIX was logarithmic. An optimal cut-off value for log2(EASIX) was determined to serve as an indicator of mortality risk under the maximally selected rank statistics. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox regression models were used to assess the link between log2(EASIX) and mortality within 1 year. Subgroup analyses were performed to ascertain the prognostic impact of log2(EASIX) in various patient groups. Mediation analysis was employed to uncover and elucidate causal pathways connecting log2(EASIX) to mortality.
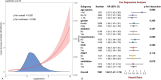
Results: It encompassed 7,901 patients. According to the Kaplan-Meier curves, increased log2(EASIX) levels correlated with a higher likelihood of all-cause mortality (p < 0.001). Cox models and subgroup analyses further revealed that groups with high log2(EASIX) levels exhibited a greater mortality risk than those with lower levels (hazard ratio (HR): 1.62, 95% CI: 1.47-1.78), a trend that persisted across most subgroups, with the exception of varying levels of APS III, body mass index, white blood cell counts, or albumin (p for interaction < 0.05 for all). Subsequent mediation analysis suggested that blood urea nitrogen and red cell distribution width partially mediated the relationship between log2(EASIX) and mortality with 17.3% and 36.5% of the mediating effect.
Conclusion: It found an independent association between elevated log2(EASIX) levels and a higher risk of 1 year all-cause mortality in ICU patients suffering from HF, with a stronger effect observed in patients with low levels of APS III or white blood cell counts, or high levels of body mass index or albumin. This association may be partially mediated by blood urea nitrogen and red cell distribution width.
Keywords: EASIX; endothelial activation and stress index; heart failure; intensive care unit; mortality.
Copyright © 2025 Yin and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

