Prospective Observational Study of Sympathetic Failure as a Mechanism Associated with Bradycardia During Induction of General Anesthesia in Children with Down Syndrome
- PMID: 40376277
- PMCID: PMC12080589
- DOI: 10.4274/jpr.galenos.2024.87528
Prospective Observational Study of Sympathetic Failure as a Mechanism Associated with Bradycardia During Induction of General Anesthesia in Children with Down Syndrome
Abstract
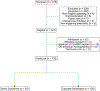
Aim: While bradycardia in children with Down syndrome (DS) during inhalation induction of anesthesia is characteristic, its mechanism is not well understood. This study investigated sympathetic failure as a potential (and modifiable) mechanism of bradycardia.
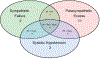
Materials and methods: Ninety-three children with DS and 102 typically developing (TD) children underwent inhalation induction of anesthesia. These children were monitored for sympathetic activity, exposed to sevoflurane anesthetic and were observed for the development of bradycardia. The primary outcome was sympathetic failure in the context of normoxic bradycardia within the first 300 seconds of induction. Secondary outcome measures included hypotension and parasympathetic excess.
Results: During the first 300 seconds of induction, 54 DS children became bradycardic (54/93, 58%) while 22 TD children became bradycardic (22/102, 22%). In the DS group, 23 experienced hypotension (23/80, 29%). Of those who experienced hypotension, 15 also experienced sympathetic failure (15/28, 54%).
Conclusion: More than half of children with DS undergoing inhalation anesthesia induction with sevoflurane experienced bradycardia. Bradycardia and hypotension were associated with sympathetic failure. Sympathetic activity therefore appears to be a modifiable target in the prevention of bradycardia in children with DS.
Keywords: Down syndrome; autonomic nervous system diseases; pediatric anesthesia; sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bradycardia during induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane in children with Down syndrome.Anesth Analg. 2010 Nov;111(5):1259-63. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f2eacf. Epub 2010 Aug 24. Anesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 20736433
-
Sedation methods for transthoracic echocardiography in children with Trisomy 21-a retrospective study.Paediatr Anaesth. 2017 May;27(5):531-539. doi: 10.1111/pan.13120. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Paediatr Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28181351
-
Cardiac and sympathetic activation are reduced in children with Down syndrome and sleep disordered breathing.Sleep. 2012 Sep 1;35(9):1269-75. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2084. Sleep. 2012. PMID: 22942505 Free PMC article.
-
Down syndrome and the autonomic nervous system, an educational review for the anesthesiologist.Paediatr Anaesth. 2022 May;32(5):609-616. doi: 10.1111/pan.14416. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Paediatr Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 35156260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sevoflurane and bradycardia in infants with trisomy 21: A case report and review of the literature.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jan;80:5-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26746603 Review.
References
-
- Kraemer FW, Stricker PA, Gurnaney HG, et al. Bradycardia during induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane in children with Down syndrome. Anesth Analg 2010; 111:1259–63. - PubMed
-
- Roodman S, Bothwell M, Tobias JD. Bradycardia with sevoflurane induction in patients with trisomy 21. Paediatr Anaesth 2003; 13:538–40. - PubMed
-
- Borland LM, Colligan J, Brandom BW. Frequency of anesthesia-related complications in children with Down syndrome under general anesthesia for noncardiac procedures. Paediatr Anaesth 2004; 14:733–8. - PubMed
-
- von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Sommerfield D, Slevin L, Drake-Brockman TFE, Zhang G, Hall GL. Effect of albuterol premedication vs placebo on the occurrence of respiratory adverse events in children undergoing tonsillectomies: The REACT randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 2019; 173:527–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai W, Voepel-Lewis T, Malviya S. Hemodynamic changes in children with Down syndrome during and following inhalation induction of anesthesia with sevoflurane. J Clin Anesth 2010; 22:592–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
