Predictive value of systemic inflammatory index (SII) for the time to negative nucleic acid conversion in patients with mild COVID-19 by the omicron wave
- PMID: 40376291
- PMCID: PMC12078121
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1474236
Predictive value of systemic inflammatory index (SII) for the time to negative nucleic acid conversion in patients with mild COVID-19 by the omicron wave
Abstract
Objective: Inflammatory indices are pivotal markers in gaging the harm of the COVID-19 trajectory. The definitive impact of inflammatory indices on forecasting the period required for a negative shift in nucleic acid status during the Omicron wave remains ambiguous. This research endeavors to delineate the relationship between the Systemic Inflammatory Index (SII) and the timeline for conversion to negative nucleic acid status in Omicron variant-infected patients, and to scrutinize the prognostic validity of SII for such conversion.
Methods: Adult patients hospitalized at the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center with mild cases attributed to the Omicron variant were studied from March to December 2022. They were stratified into early-conversion (with mild cases attributed to (>10 days) groups). Analyzing patient information, clinical traits, and laboratory results, we divided patients into two groups. We used logistic regression to find the link between SII and virus test timing and built ROC curves to measure predictive value via AUC.
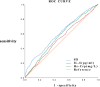
Results: A total of 2,603 patients were enrolled. Univariate analysis found big differences in pulse rates, respiratory rates, prealbumin levels, HS-CRP levels, IL-6 levels, SII, and PNI (p < 0.05) between the groups. Adjusting for confounders, logistic regression revealed that the highest SII group had a 1.46 greater risk of not clearing a 10-day PCR test than the lowest group (OR = 1.46; 95% CI, 1.173-1.817, p = 0.001). Each one-unit rise in SII raised the risk of 10-day PCR failure by 0.1% (p < 0.0001). The ROC curve showed SII's AUC as 0.603 (95% CI: 0.576-0.630), predicting virus test turn-around with a cut-off of 920.5, 61.9% specificity, and 52.5% sensitivity. Compared to other indicators such as IL-6 and HS-CRP, SII exhibited the highest AUC value and specificity.
Conclusion: In mild cases caused by the Omicron wave, there was a discernible link between the SII and the period leading to a negative nucleic acid test outcome, with higher SII values indicating an increased risk of prolonged conversion time. SII might help guide treatment better than other indicators by predicting disease course.
Keywords: AUC; COVID-19; nucleic acid negative time; omicron variant; systemic inflammatory index.
Copyright © 2025 Fan, Yang, Zhuo and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Z, Deng X, Fang L, Sun K, Wu Y, Che T, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and transmission dynamics of the outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant in Shanghai, China: a descriptive study. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. (2022) 29:100592. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100592 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous