Novel anoikis-related genes for the diagnosis of non-obstructive azoospermia
- PMID: 40376522
- PMCID: PMC12076243
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-2024-745
Novel anoikis-related genes for the diagnosis of non-obstructive azoospermia
Abstract
Background: Non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) is a prevalent cause of male infertility, featured by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate due to impaired spermatogenesis. The involvement of anoikis in the pathogenesis of NOA remains inadequately understood. This research aims to identify anoikis-related genes as potential biomarkers for NOA diagnosis.
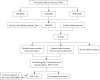
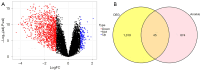
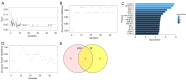
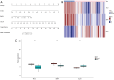
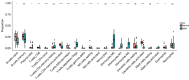
Methods: Based on the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and Limma R package, we identified differentially expressed genes of NOA and downloaded anoikis-related genes based on the GeneCards database. Subsequently, anoikis-related hub genes were screened by machine learning (ML), and validated using external validation sets. A nomogram constructed from these genes demonstrated high predictive accuracy, while boxplots and complex heatmaps illustrated the differential expression patterns observed in NOA samples. Additionally, immune infiltration analysis was performed using the CIBERSORT algorithm to evaluate the distribution of immune cells in both NOA and control groups. The validation of candidate genes was conducted through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, with the area under the curve (AUC) indicating predictive accuracy.
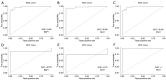
Results: Ultimately, we screened three hub genes: GLO1, BAP1, and PLK1. GLO1 was found to be up-regulated, while both BAP1 and PLK1 were down-regulated. Immune cell infiltration analysis elicited significant differences in 16 immune cell types between NOA patients and normal controls, with Tregs and macrophages notably up-regulated in NOA. ROC analysis indicated that all the three hub genes exhibited excellent diagnostic efficacy. Specifically, ROC curve analysis confirmed the diagnostic potential of GLO1, BAP1, and PLK1, yielding AUC values of 0.981, 0.980, and 0.981 in internal datasets, and 0.750, 0.875, and 1.000 in external datasets.
Conclusions: By ML analysis, this research identified three anoikis-related genes that may be diagnostic biomarkers for NOA, offering views into the underlying molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Anoikis-related genes; non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA); random forest (RF); support vector machine (SVM).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-2024-745/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and validation of SHC1 and FGFR1 as novel immune-related oxidative stress biomarkers of non-obstructive azoospermia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 26;15:1356959. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356959. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39391879 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying potential biomarkers for non-obstructive azoospermia using WGCNA and machine learning algorithms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 3;14:1108616. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1108616. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37854191 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analyses of potential biomarkers and pathways for non-obstructive azoospermia.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 24;13:988047. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.988047. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36506310 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers associated with macrophage infiltration in non-obstructive azoospermia using single-cell transcriptomic and microarray data.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):55. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5601. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819497 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Successful Testicular Sperm Extraction: A New Era for Men with Non-Obstructive Azoospermia.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 25;12(12):2679. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122679. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
